Joining Or Leaving A Domain
If your computer is part of a domain, joining or leaving the domain wont generally be your job. If your computer needs to be on a domain, it will already be on a domain when its handed to you. Youll usually need the domain administrators permission to leave a domain, so people who sit down to use a domain-joined PC cant just leave the domain. However, you can leave a domain if you have local administrator access on your PC. You wont have administrator access if youre using a locked-down PC, of course.
If you have an old computer thats joined to a domain and you no longer have access to the domain, you can always gain access to the PC by reinstalling Windows. The domain settings are tied to your installed operating system, and reinstalling Windows will give you a fresh system. You shouldnt do this to a work or school PC you dont own, of course!
Domains limit what you can do on your PC. When your computer is part of a domain, the domain controller is in charge of what you can do. This is why theyre used on large corporate and educational networks they provide a way for the institution that provides the computers to lock them down and centrally administer them.
Thats the core concept, although much more can be done with domains. For example, group policy can be used to remotely install software on computers joined to a domain.
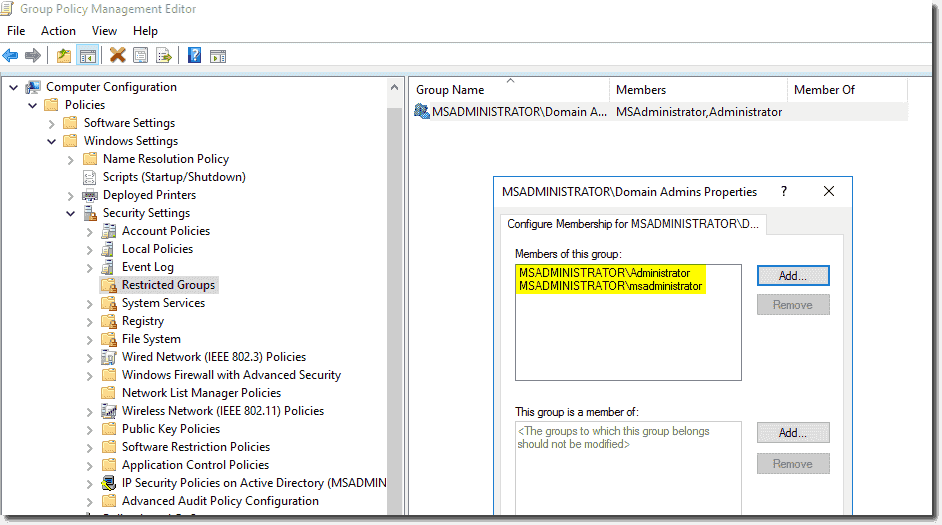
Limit The Number Of Domain Admin Accounts And Who Has Access To Them
Ideally, as stated previously, this should be limited to zero accounts except for the default Administrator.
When contemplating the need for a Domain Admin account, consider the follow:
- Why is it needed?
- Can the same thing be achieved with a non-domain admin account?
- Are you avoiding best practice for the sake of ease?
- Who is going to be responsible for monitoring the account usage and decommissioning it when it is no longer required?
Remember that generic accounts for interactive device usage are poor practice as they essentially anonymise the actions of the person using said account. If two or more people have access to a single account then they each have plausible deniability for any wrong-doing that occurs from that account.
What Is A Windows Domain And How Does It Affect My Pc
Chris Hoffman
Chris Hoffman is Editor-in-Chief of How-To Geek. He’s written about technology for over a decade and was a PCWorld columnist for two years. Chris has written for The New York Times and Reader’s Digest, been interviewed as a technology expert on TV stations like Miami’s NBC 6, and had his work covered by news outlets like the BBC. Since 2011, Chris has written over 2,000 articles that have been read nearly one billion times—and that’s just here at How-To Geek. Read more…
Windows domains are typically used on large networks corporate networks, school networks, and government networks. They arent something youll encounter at home unless you have a laptop provided by your employer or school.
A typical home computer is an isolated entity. You control the settings and user accounts on the computer. A computer joined to a domain is different these settings are controlled on a domain controller.
Don’t Miss: How To Find Out Where My Domain Name Is Registered
Least Privilege For Administrators On Domain
I have been looking into this more seriously of late but I am not sure how, or even if I can implement for Domain Administrators.
I am the main admin for my workplace, but also have a few others who have Domain Admin accounts.
Every user has a simple domain user account which isn’t granted access to any of our servers. When I access our servers I use my specific admin account for it. When I access my local computer I use my normal domain account for it.
How can I implement least privilege for these accounts if the are needed to administer our Domain servers?
Thanks.
Popular Topics in General IT Security
At my last organization we had different levels of administration. Help desk guys were able to reset passwords, others needed to join machines to the domain and some needed Domain Admins privileges. As Richardwright2 mentioned above you have to create OUs if you want to differentiate any permissions. Then you need to delegate the desired permissions to the desired OUs.
I’ll say that if a user needs to join computers to the domain nothing short of domain admins will work. We spent a lot of time trying to get around that. Had serious issues with domain joins and renaming computers. We had to make them Domain Admins.
Here is a good thread on delegating permissions.
Delegate Admin Privileges
It Leaves Password Hashes Everywhere
Windows provides authentication throughout the network by passing around hashes of the account password, rather than the password itself. These hashes are stored locally in the Windows SAM file and can be copied and cracked by someone with sufficient skill. If a domain admin or similarly high-privileged account gets compromised, you are, for lack of a better term, screwed. At this point you would have two options available:
You May Like: How Much Does A Custom Domain Cost
Domain Accounts For Remote Support
If you are not able to use local accounts, the alternative is to use domain accounts. Instead of adding accounts to the Domain Admins group, one option is to create a group for each domain-joined device, configure Group Policy Preferences to add the groups to the devices, and then add IT staff accounts to the new domain groups as needed. The process of creating groups can be automated using PowerShell.
While this isnt as bulletproof as using unique local accounts on each device, creating domain groups is more secure than adding accounts to the Domain Admins group. You just need to watch out for token bloat if you add users to many groups.
How To Become A Domain Administrator
There is more than meets the eye when it comes to being a domain administrator. For example, did you know that they make an average of $39.52 an hour? That’s $82,208 a year!
Between 2018 and 2028, the career is expected to grow 5% and produce 18,200 job opportunities across the U.S.
You May Like: How To Set Up An Email With Your Domain
Eliminate Use Of Administrator Accounts
If you are currently using domain admin privileges for managing AD, servers, and end-user devices, devise a plan to remove that access and delegate control to protect Active Directory and other systems from attack or accidental changes. If you want to completely remove administrator rights, a third-party Privileged Access Management solution, such as those provided by BeyondTrust, can help you completely and efficiently eliminate use of administrator accounts.
How Do I Log Into My Domain Account
How to logon to a domain controller locally?
Also Check: How To Find Your Domain Registrar
Finding Domain Admin Processes
Ok, enough of my ramblings. As promised, below are 5 techniques for finding Domain Admin processes on the network.
Technique 1: Checking Locally
Always check the initially compromised system first. Theres really no point is running around the network looking for Domain Admin processes if you already have one. Below is a simple way to check if any Domain Admin processes are running using native commands:
It would be nice if Domain Admin processes were always available on the system initially compromised, but sometimes that is not the case. So the next four techniques will help you find Domain Admin process on remote domain systems.
Technique 2: Querying Domain Controllers for Active Domain User Sessions
Technique 3: Scanning Remote Systems for Running Tasks
The original post is: Crawling for Domain Admin with Tasklist if youre interested.
Technique 4: Scanning Remote Systems for NetBIOS Information
Technique 5: PSExec Shell Spraying Remote Systems for Auth Tokens
How To Manage Windows Without Domain Admin Privileges
Active Directory is a gateway for hackers to your entire IT infrastructure. Despite this, IT staff are routinely granted privileged access to Active Directory, which leaves the environment susceptible to threats, and may allow malicious actors to infiltrate the deepest levels of your infrastructure, while hiding their tracks. But a few, simple Active Directory security best practices can significantly reduce the risk of a breach.
The principle of least privilege is a well-known security paradigm that dictates users should be granted only the rights required to perform designated tasks. IT staff are often given domain admin privileges to Active Directory to expedite access to domain controllers and administrative access to servers and end-user devices. But domain admin privileges are not required for managing Active Directory or for supporting servers and workstations. When domain admin rights are required, they should be granted for a time-limited period, and only used on systems secured to the same standards as domain controllers.
Want to learn more? Join me in my webinar “8-Step Guide to Administering Windows without Domain Admin Privileges”
You May Like: How Do You Find Who Owns A Domain
Best Practices For Managing Domain Admin Accounts
Auditors often discover that domain administrator privileges are assigned to IT staff with abandon, and not strictly limited to the just-in-time use on domain controllers that Microsoft and security experts recommend. This is partly due to the default local group configuration on Windows clients, where domain administrators automatically become members of the local Administrators group when a device joins a domain, which in turn gives the local and remote access needed to support end users. In a similar vein, the same applies to domain member servers.
Check out this on-demand webinar on best practices for managing domain admin accounts to learn pro-tips to protect your organization from critical attacks.
The risks of using privileged domain accounts on devices that are not secured to the same level as DCs increases the chances that domain administrator credentials could be exposed. Windows caches credentials by default to authenticate users when a domain controller cant be reached, including those of domain administrator accounts that have previously logged in to a device. As such, a compromised workstation or member server can also lead to stolen domain administrator credentials.
Want to learn more? Watch this on-demand webinar now.
About Active Directory Groups
Groups are used to collect user accounts, computer accounts, and other groups into manageable units. Working with groups instead of with individual users helps simplify network maintenance and administration.
There are two types of groups in Active Directory:
-
Distribution groups Used to create email distribution lists.
-
Security groups Used to assign permissions to shared resources.
Also Check: When Will Domain Become Available
Terminal Server License Servers
Members of the Terminal Server License Servers group can update user accounts in Active Directory with information about license issuance. This is used to track and report TS Per User CAL usage. A TS Per User CAL gives one user the right to access a Terminal Server from an unlimited number of client computers or devices. This group appears as a SID until the domain controller is made the primary domain controller and it holds the operations master role .
For more information about this security group, see Terminal Services License Server Security Group Configuration.
The Terminal Server License Servers group applies to versions of the Windows Server operating system listed in the Active Directory Default Security Groups table.
Note
This group cannot be renamed, deleted, or moved.
This security group only applies to Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008 because Terminal Services was replaced by Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2008 R2.
| Attribute |
|---|
| None |
Techopedia Explains Administrative Domain
A good example is a corporate network that spans different regions and is managed by a single office or department. The components within the administrative domain operate mostly with mutual trust and treat all outside entities with suspicion. For large corporations with various offices scattered across the world, this allows the efficient sharing of data and dissemination of information, without strict security interfering with the communication network. Information is typically safe from outsiders, but the real threat comes from inside the domain, specifically when it comes to sending information to outside entities.
Recommended Reading: Where To Buy Cheap Domains
How Do I Find My Domain Username And Password
How to Find a Domain Admin Password
Windows Authorization Access Group
Members of this group have access to the computed token GroupsGlobalAndUniversal attribute on User objects. Some applications have features that read the token-groups-global-and-universal attribute on user account objects or on computer account objects in Active Directory Domain Services. Some Win32 functions make it easier to read the TGGAU attribute. Applications that read this attribute or that call an API that reads this attribute do not succeed if the calling security context does not have access to the attribute. This group appears as a SID until the domain controller is made the primary domain controller and it holds the operations master role .
The Windows Authorization Access group applies to versions of the Windows Server operating system listed in the Active Directory Default Security Groups table.
Note
This group cannot be renamed, deleted, or moved.
This security group has not changed since Windows Server 2008.
| Attribute |
|---|
| None |
Recommended Reading: How To Negotiate A Domain Name
S To Enable Auditing Using The Group Policy Management Console :
Perform the following actions on the domain controller :
Once this policy is enabled, whenever a user is added to the security-enabled group, corresponding events are logged under the DC’s security log category.
Use Managed Service Accounts For Scheduled Tasks And Services
When deploying scheduled tasks or custom/third party services to devices, it is recommended that you create a unique Managed Service Accounts for each one to compartmentalise and limit potential attack vectors.
Managed Service Accounts are a sort of hybrid computer and user account, but inherit mainly from computer accounts, so they will automatically update their passwords on the same scheduled as a computer account . They are also incapable on interactive logins.
Read Also: How To Add User To Domain Windows 10
Denying Access To Devices
So now that you have some background on the credential Tier model and understand why it is important to prevent privileged users from authenticating on untrusted devices, let’s look at some of the ways enterprises can control Tier 0 accounts from logging onto lower Tier devices.
- Define a policy and trust your Domain Administrator’s to follow the rules.
- This never works. Prior to working for Microsoft and while working with customers I see this model fail. Admins always try to justify the practice of not protecting the credentials with not enough time to do the proper protection.
- Deny logon via RDP