Dns Servers And Ip Addresses
Each domain can correspond to more than one IP address. In fact, some sites have hundreds or more IP addresses that correspond with a single domain name. For example, the server your computer reaches for is likely completely different from the server that someone in another country would reach by typing the same site name into their browser.
Another reason for the distributed nature of the directory is the amount of time it would take for you to get a response when you were looking for a site if there was only one location for the directory, shared among the millions, probably billions, of people also looking for information at the same time. Thats one long line to use the phone book.
What Is Dns Domain Name System Explained
DNS, short for Domain Name System, is one of the most common yet misunderstood components of the web landscape. To put it simply, DNS helps direct traffic on the Internet by connecting domain names with actual web servers. Essentially, it takes a human-friendly request a domain name like kinsta.com and translates it into a computer-friendly server IP address like 216.3.128.12.
Kinstas hosting receives hundreds of five-star ratings. Every Day.
Really love the level of experience and support Kinsta’s live chat engineers provide. The 24/7 support is a game-changer for large sites, especially ecommerce.
Because DNS is all about looking up addresses and connecting devices, many people call DNS the phonebook of the Internet. Without DNS, youd have to memorize every sites IP address to access it whichwell, that just wouldnt work!
Lets talk about these four components and how they work together.
How To Flush Dns
Operating systems like Windows and others will store IP addresses and other information about hostnames locally so that they can be accessed quicker than having to always reach out to a DNS server. When the computer understands that a certain hostname is synonymous with a certain IP address, that information is allowed to be stored, or cached on the device.
While remembering DNS information is helpful, it can sometimes become corrupted or outdated. Normally the operating system removes this data after a certain period of time, but if you’re having troubles accessing a website and you suspect it’s due to a DNS issue, the first step is to force-delete this information to make room for new, updated DNS records.
You should be able to simply reboot your computer if you’re having troubles with DNS because the DNS cache isn’t retained through a reboot. However, flushing out the cache manually in place of a reboot is much quicker.
You can flush the DNS in Windows through Command Prompt with the ipconfig /flushdnscommand. The website What’s My DNS? has instructions on doing this on macOS and Linux.
It’s important to remember that, depending on how your specific router is set up, DNS records might be stored there, too. If flushing the DNS cache on your computer doesn’t fix your DNS problem, you should definitely try restarting your router to flush that DNS cache.
Read Also: How Much Do Domains Cost Per Year
Whats Next For The Dns
When we think about the future of the DNS, we think about securityand thats where domain name system security extensions come into play.
Its important for DNS resolvers to verify that the data theyre requesting originates from where it says and to confirm that information hasnt been intercepted or modified in transit. DNSSEC does this by using digital signatures, which secure every DNS zone with public and private DNS keysmaking the internet a safer place to browse.
In addition, adopting DNSSEC is a crucial step toward achieving Zero Trust security. As cloud and mobile adoption continues to grow, businesses can no longer take a network perimeter-centric approach. Instead, they need to enable secure access to several types of usersfrom employees to partners and contractorsregardless of their location, device, network, or DNS server. With this approach, only the right people have the right level of access to the right resources in the right context.
What Is The Dns
The Domain Name System is a bit like a postal service. There are millions of DNS servers carrying DNS records information to users about the websites they are visiting. Each server in the delivery chain needs to be up-to-date with the latest information within the DNS records.
Servers that contact your website regularly save relevant DNS records to help everything work smoothly. This process is a bit like jotting down favorite addresses for safe-keeping. These handy records include, but are not limited to, your DNS hosting address or nameserver record.
For the full lowdown on the DNS system, read our excellent blog What is DNS?
Recommended Reading: How To Transfer My Domain From Wix To Shopify
What Is The Difference Between Dnssec And Dns Security
The difference between DNSSEC vs. DNS security is that DNSSEC refers to the new protocol ensuring the validity of DNS queries, data and results with the help of cryptographic signatures. DNS security refers to the concept that organizations, companies, users and services can use DNS to secure networks.
The Domain Name System
During the internets formative years, IP addresses were ingenious creations, allowing computer scientists to identify individual computers, and to communicate between them. While this worked quite well when the internet was composed of just a few computers, as more devices and people joined the rapidly growing network, this method, understandably, grew overly complicated.
As you might imagine, if this was difficult for computer scientists, asking introductory users to memorize multiple strings of 12 random digits was impractical, if not impossible. While it would have been possible to create a gigantic IP phone book of sorts, each with the specific computer and IP address, this too seemed an inefficient solution. So, to alleviate this problem, computer scientists proposed the creation of a domain name system.
The root idea underlying the concept of DNS was that humans have an easier time remembering words than numerical strings. Therefore, it would be much simpler to have a nickname for each IP address, which we now call, a domain name. To facilitate this process, each domain name would be:
- A unique, one-of-a-kind, name linked to a specific IP address.
- Registered, maintained, and paid for by the owner.
- Added to an extensive directory to be regulated and overseen.
This proposed solution was widely embraced, and the domain name system was born.
You May Like: How Much Does It Cost To Own A Domain
For Advanced Users Of Dns Records
A quick note before we startif you are more confident about DNS records or perhaps a Namecheap customer, you may not wish to read everything below. You might find these short technical articles the help you need to check how to adjust your DNS records.
- How to create a CNAME record for your domain domains using our three DNS services above can set CNAME records in their account panel, or if you are with Namecheap web hosting DNS, watch this video.
Need more than this? Then lets begin with an explanation of the DNS.
Every Website Has Dns Records
Type any website name into a browser, and the browser tracks down your websites nameserver record. This translates your IP address, which is a series of numbers, into a word addressyourdomainname.comwhich is far easier to remember. Once this is done, a user can see your website.
Anyone looking for your website on the Internet will need your NS record to verify they have found the actual website. All this happens out of sight. A user is not aware that theyve set a DNS process into action when they type in your web address.
The browser check will find these other DNS records, too :
- A records will point to a specific IP Address.
- CNAME records will point a domain or subdomain to another domain.
- MX Records show which email client you are using.
- TXT Records deliver security, verification, and data analysis information.
So every domain needs the DNS running in the background. Its how you find a website and securely interact with whatever software is running on the page.
Who runs the DNS for your website? When the DNS began, the system was much smaller. If you think about it, todays domain name system comprises many serversnot just nameservers communicating with each other. All these DNS servers need to agree with each others databases to validate your website domain, or else youll get a website not found error. Nowadays, one needs to carefully choose a DNS provider, because if the provider is not reliable, then the chances that a website will be unstable are high.
Recommended Reading: Transfer Wix Domain To Shopify
Commercial Vs Enterprise Needs
For most individuals or even small businesses, a commercial-level purchase of a domain name is all they will ever really need to think about. This means buying an available domain name , configuring the domain name with the web hosts nameservers, and going about your business.
On an enterprise level, though, DNS has many more considerations for organizations to consider. Relying on a providers DNS creates various limitations. For example, this centralizes DNS, but for a company dealing with international traffic, geographic distances can slow down response times. This may be even more critical if youre going beyond a web page and into an app that has to process queries/responses to an international userbase. This combination of physical distance and centralized DNS creates a single point of failure to generate lengthy timeouts . An enterprise DNS setup uses a dedicated network, usually with geographically diverse locations. This creates many layers of redundancy and geographic efficiency for handling traffic, even when there is a server issue.
Security is also a concern, as unencrypted DNS communication can lead to malware and other dangerous encounters. Enterprise DNS services often have protection protocols for Distributed Denial of Service attacks, providing multiple layers to mitigate the impact of attack while keeping domains accessible.
How Does Dns Work
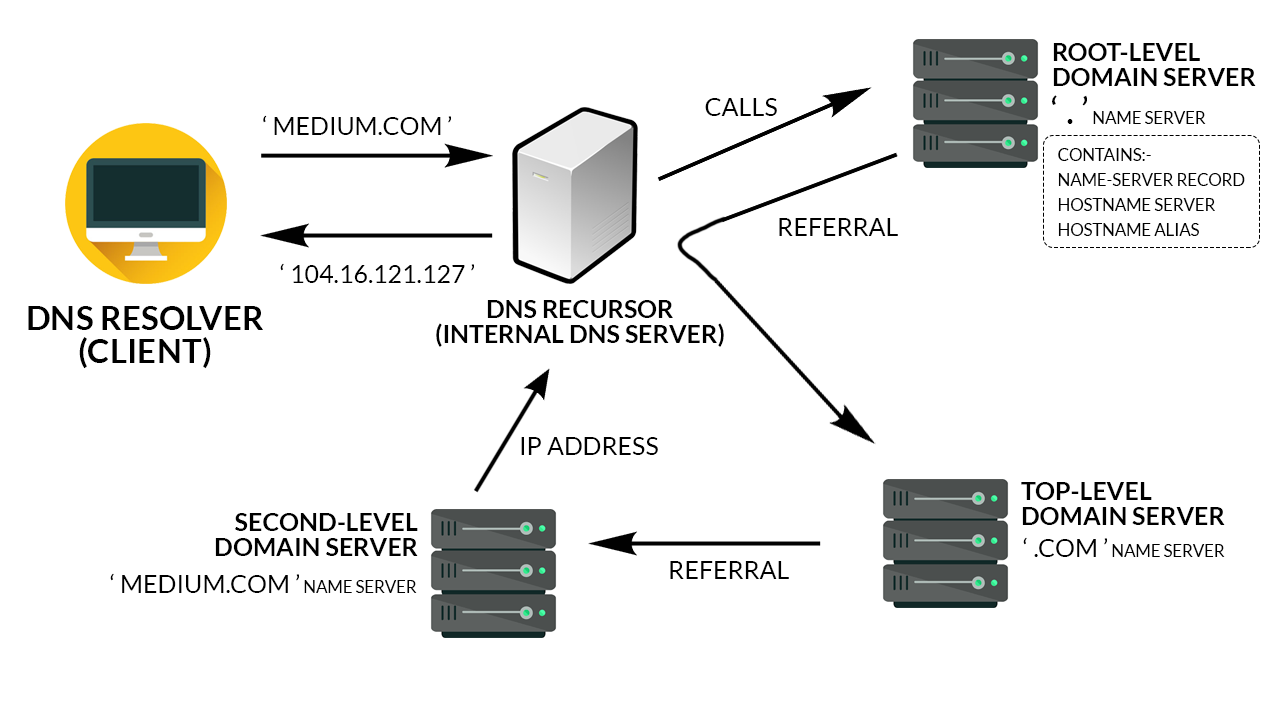
Before we get into how you can use the DNS, we need to understand how the system works. We already know that it maps IP addresses to domain names, but where is this information stored? On nameservers!Nameservers store DNS records which are the actual file that says âthis domainâ maps to âthis IP addressâ. So is there a room somewhere that has all the nameservers and DNS records for every site on the Internet? No⦠that would be ridiculous.â
They are actually distributed all around the world. These nameservers are called the root nameservers and instead of storing every domain ever, they store the locations of the TLD .TLDâs are the two or three character like .com that end a domain name. Each TLD has their own set of nameservers that store the information that says who is authoritative for storing the DNS records for that domain.The authoritative nameserver is typically the DNS provider or the DNS registrar . And here we can find the DNS record that maps example.com to the IP address 127.66.122.88.
Want a Proof of Concept?
Start your free 30 day trial and have access to the fastest and most reliable DNS in the world.â
- 11490 Commerce Park Dr Ste 140Reston, Virginia 20191 USA
Recommended Reading: Transfer Godaddy Domain To Wix
Domain Name System Vs Domain Name Server
For the casual user, it can be very easy to confuse domain name system and domain name server with the acronym DNS. What is the difference? DNS properly stands for domain name system domain name server technically is not a true term. Instead, people tend to mean nameservers, which are the local DNS servers used to resolve queries about local names. The domain name system refers to a larger, more-encompassing system for translating domain names and IP addresses as part of a multi-step process. Both the DNS process and the roles of various domain name servers are described below.
Performing A Dns Lookup
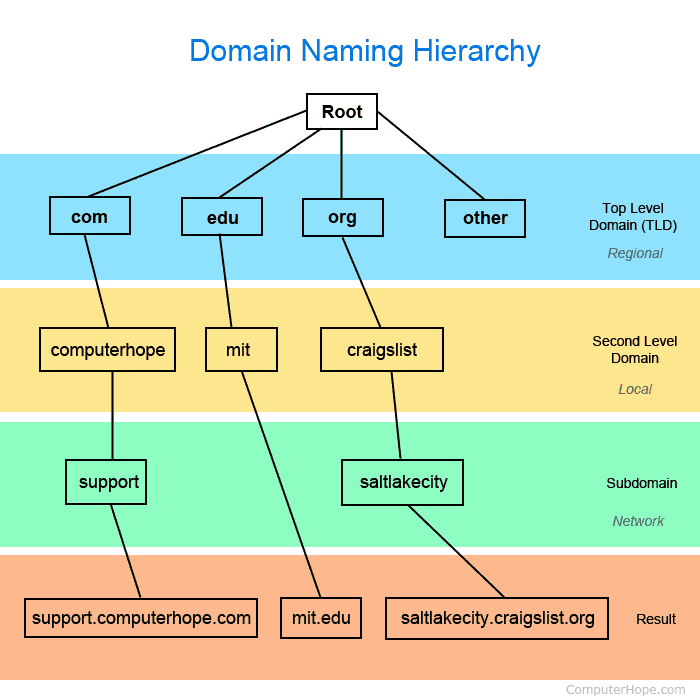
A Domain Name System lookup is simply the process involved in resolving a domain name into its IP address or vise versa. These are of two types forward and reverse DNS lookup.
Forward DNS lookup also referred to as normal DNS lookup involves resolving a domain name into its IP address. While reverse lookup does the opposite, it resolves an IP address into its corresponding domain name.
Here, we will focus on the forward lookup simply because thats the default lookup most websites perform.
Don’t Miss: How To Find Email Domain And Server
What Is Dns How It Works + Vulnerabilities
The Domain Name System is the internets version of the Yellow Pages. Back in the olden times, when you needed to find a business address, you looked it up in the Yellow Pages. DNS is just like that, except you dont actually have to look anything up: your internet connected computer does that for you. Its how your computer knows how to find , or ESPN.com, or Varonis.com.
For two computers to communicate on an IP network, protocol dictates that they need an IP address. Think of an IP address like a street address for one computer to locate another, they need to know the other computers number. Since most humans are better at remembering names www.varonis.com than numbers 104.196.44.111, they needed a program for computers to translate names into IP addresses.
Difference Between Domain And Dns
The main difference between domain and DNS is that the domain is a piece of string that helps to identify a particular website while the DNS is a server that translates the domain to the corresponding IP address to provide the required webpage.
There are many websites on the World Wide Web including education, e-commerce, government, entertainment sites. It is necessary for each website to have a domain name. It helps to identify the website. The domain is unique to a particular user and others cannot use that name for their websites. When the user enters a domain in the browser, the DNS converts that name to the matching IP address to provide the required webpage. In brief, DNS resolves the domains to IP addresses.
Don’t Miss: Cost Of Purchasing A Domain Name
What Is Domain Name System
Domain Name System is a hierarchical naming system built on a distributed database for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. Most importantly, it translates human readable domain names into the numerical identifiers associated with networking equipment, enabling devices to be located and connected worldwide. Analogous to a network phone book, DNS is how a browser can translate a domain name to the actual IP address of the server, which stores the information requested by the browser.
DNS Basics
The domain name system is responsible for translating domain names into a specific IP address so that the initiating client can load the requested Internet resources. The domain name system works much like a phone book where users can search for a requested person and retrieve their phone number. DNS servers translate requests for specific domains into IP addresses, controlling which server users with access when they enter the domain name into their browser.
A Brief History of DNS
As the Internet grew to millions of domains, this was not sustainable. In 1983, Paul Mockapetris, a USC researcher, was tasked with developing a solution. His solution was a new system that he named DNS, which remains based on Mockapetris fundamental principles. Today, the standards for DNS are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force in RFC 1035.
How DNS Servers Work
DNS servers and IP addresses
The DNS Lookup Process
Types of DNS Services