Domain Owners: Outlookcom With Microsoft 365 Family/personal Or Microsoft 365 Exchange Online
When you own a domain and also have a Microsoft 365 Family/Personal subscription, then you can link your domain to Outlook.com so that everyone in your subscription can also use a personalized address with their Outlook.com mailbox .
The benefit of this method is that you dont have to configure any forwarder or Send Only POP3 account. You are however limited to only 1 personalized address per Outlook.com mailbox. The Microsoft 365 Family subscription allows up to 6 people with such a personalized address whereas the Microsoft 365 Personal subscription only allows 1.
To set this up, the one managing the Microsoft 365 Family/Personal subscription will have to do this in Outlook.com via
- Settings-> View all Outlook settings-> Premium-> Features-> Personalized email address
Currently, this benefit is only possible when GoDaddy is the registrar for your domain.
Setting up a personalized email address via Outlook.com Premium.
How Dns Route Traffic To Your Web Application How Dns Works
Thousandeyes Offer Network Intelligence Into Dns
ThousandEyes is a network intelligence platform that delivers visibility into every network an organization relies on, enabling organizations to optimize and improve application delivery, end-user experience, and ongoing infrastructure investments.
This is made possible through the ThousandEyes SaaS platform that allows customers to test application and network performance against assets owned by the organization, and assets owned by the organization’s Service Providers . These tests are executed using Endpoint Agents, Enterprise Agents and Cloud Agents and comprised of Network Tests, DNS Tests and Web Tests.
Additional Learning
Don’t Miss: What Is The Io Domain Used For
Summary Of Name Server Vs Dns
In a nutshell, DNS is a hierarchical distributed database for translating domain names into their corresponding IP addresses. Every time you type a web address, send a mail, or access just any IP application, you use DNS. Name server is a server that runs DNS software and manages all the domain name records. DNS solves three basic problems, organization, scalability, and management. The DNS uses a hierarchical name structure and its layers are arranged in a definitive order, and its data is distributed across a range of machines, each of which can enact control over a portion of the database.
What Is A Nameserver A Complete Guide To Nameservers
With the increasing demand for websites, more and more people are searching for terms like what is a nameserver? If you are building your website you must have come across the term nameserver. In this article, we will learn all about domain name servers and try to find all the answers to your doubts.
In this article, we will cover the topics like
Also Check: Transfer Wix Domain To Squarespace
Difference Between Hostname And Server Name
Categorized under Technology | Difference Between Hostname and Server Name
The Domain Name System is fundamental to proper functioning of virtually all Internet Protocol network applications, from the basic emails to web scrolling to multimedia applications, and so on. Each time you type the web address of a site on your web browser or send an email to someone, you use DNS. It is a hierarchical name resolution system created to translate the website names into their corresponding IP addresses that the local host needs to communicate via the World Wide Web. And the TCP/IP is the universally recognized communications protocol for linking diverse computer systems. Name servers are an important part of the DNS, which act like a database of the devices and IP addresses linked to them. A hostname is a name assigned to a device connected to a network.
What Is A Nameserver And Its Purpose
NS stands for the nameserver. NS records are the nameserver records that contain the information of the nameservers associated with the domain.
These are the DNS records type that indicates
An example of an NS record may look like the following.
| Record |
|---|
- mydomain.com represents the domain of the record
- NS represents the DNS record type.
- ns1.mydomain.com represents the value of the record. That is the nameserver for that domain.
- 3600 is TTL . It is the time for which the DNS server caches the record. On the expiry of that time, the server goes for the fresh DNS records data.
The nameserver can never point to the canonical name record.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Money With Domains
What Is Dns Used For
- Resolving names of World Wide Web sites
- Routing messages to email servers and webmail services
- Connecting app servers, databases and middleware within a web application
- Virtual Private Networks
- Global server load balancing – fast routing of connections between globally distributed data centers
- Multi CDN – routing users to the CDN that will provide the best experience
- Geographical routing – identifying the physical location of each user and ensuring they are routed to the nearest possible resource
- Data center and cloud migration – moving traffic in a controlled manner from on-premise resources to cloud resources
- Internet traffic management – reducing network congestion and ensuring traffic flows to the appropriate resource in an optimal manner
Microsoft 365 Exchange Online
When you want to host more than 6 email accounts at Outlook.com or want it to handle all the emails for your entire domain, add aliases, distribution groups and shared mailboxes, then switching to Microsoft 365 Exchange Online might be the better solution even though this isnt free .
When you choose to go this route, you dont have to configure Outlook.com to collect your mail via POP3 or configure any forwarder Mail is then being received instantly as if it was a native domain of Outlook.com itself.
The costs depend on the country that you live in but currently a single mailbox costs $4 per month. As the domain owner, this also provides you with lots of management options and you have the additional benefit of being able to share email, calendar and contact folders between your colleagues as well as creating shared mailboxes. You can find out more here: Compare Microsoft Exchange Online plans.
A better deal might be the Microsoft 365 Business Basic subscription for $5 per month. In addition to the above benefits, it will also grant each user with 1TB of online storage , Office Online, Teams and a collaboration website . The Microsoft 365 Business Standard subscription for $12.50 per month also includes the Office apps for Windows 10 and Mac.
You May Like: What Is The Io Domain Used For
What Is A Nameserver
A Nameserver is an integral part of the Domain Name System , which is popularly known as the Directory of IP Addresses. It refers to the address of the server where you want to host your website. A domain name needs to be resolved into a valid IP address of a physical server to open a website. A nameserver is the address of that web server.
Without a nameserver, it would have been almost impossible to access a website, even if they exist. Imagine if there was no concept of Nameserver, users might have to remember and enter the lengthy IP addresses in their web browser whenever they want to go to a certain website.
How difficult or nearly impossible it would have been to memorize the IP addresses of hundreds of websites that a person regularly browses. How search engines like Googles search page would have looked like in the absence of a domain name or nameservers.
A website is a set of files, and sometimes a combination of files and databases. These files and databases are hosted on a server. So, ideally, when a user wants to look at a website he will be accessing these files/database stored at a particular server. To make it possible when a user enters a web address, the request is redirected to the specific web server. Name Server makes it possible to redirect the request to that server, using its IP address.
Every valid Name Server is associated with the IP address of that server. So, this is how it all works:
Cctld: Country Code Top Level Domains
ccTLDs use just two letters and are based upon international country codes, such as .us for the United States and .jp for Japan. Theyre often used by companies that are building dedicated sites for specific regions and can be a good way of signaling to users that theyve arrived at the right place.
Read Also: How Much Should A Domain Name Cost Per Year
Domain Management: How To Update Nameservers
Domain Name System is the system that translates a domain name into an IP address. DNS forms the foundation for the Internet. DNS records are used to map each web service to the correct server. Each domain name has a collection of DNS records called a zone file. A Nameserver is a computer where DNS Records are stored. Domains will utilize the DNS records of the name server that they’re pointing to. A more in-depth look at DNS Records.To learn how to update your Nameservers, please follow the steps below and click image to enlarge:
There are two views in the Domains dashboard – the Card and List views. Click on the view icons to switch to your preferred view.
In the List view, click the domain or its gear icon on the right-hand side.
Pro Tip:
Business Email: 8 Ways You’re Using It Wrong

Its easy to get started with an email domain, and its just as easy to create new email aliases and mailboxes. However, beginners sometimes make these mistakes when they set up their business email:
You May Like: How To Get Free Net Domain
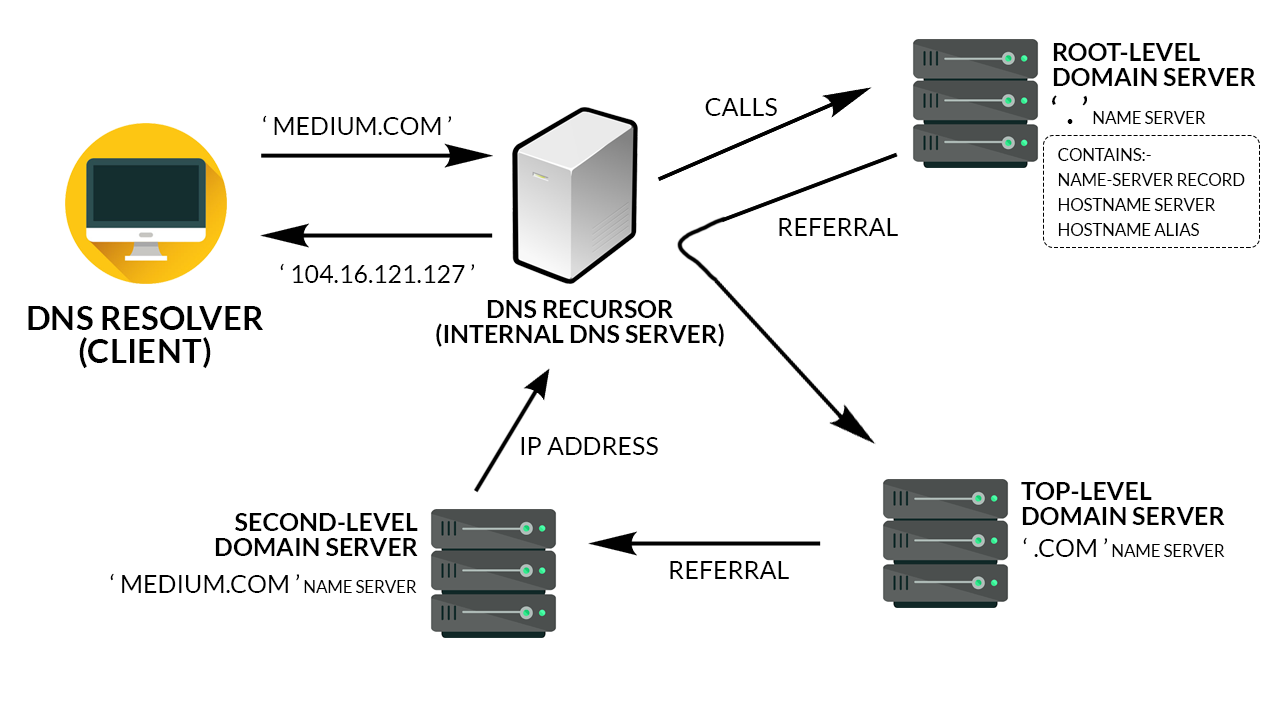
How Do Dns Servers Resolve A Dns Query
In a typical DNS query without any , there are four servers that work together to deliver an IP address to the client: recursive resolvers, root nameservers, TLD nameservers, and authoritative nameservers.
The DNS recursor is a server that receives the query from the DNS client, and then interacts with other DNS servers to hunt down the correct IP. Once the resolver receives the request from the client, the resolver then actually behaves as a client itself, querying the other three types of DNS servers in search of the right IP.
First the resolver queries the root nameserver. The root server is the first step in translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses. The root server then responds to the resolver with the address of a DNS server that stores the information for its domains.
Next the resolver queries the TLD server. The TLD server responds with the IP address of the domains authoritative nameserver. The recursor then queries the authoritative nameserver, which will respond with the IP address of the origin server.
The resolver will finally pass the origin server IP address back to the client. Using this IP address, the client can then initiate a query directly to the origin server, and the origin server will respond by sending website data that can be interpreted and displayed by the web browser.
There Are 4 Dns Servers Involved In Loading A Webpage:
- – The recursor can be thought of as a librarian who is asked to go find a particular book somewhere in a library. The DNS recursor is a server designed to receive queries from client machines through applications such as web browsers. Typically the recursor is then responsible for making additional requests in order to satisfy the clients DNS query.
- Root nameserver – The is the first step in translating human readable host names into IP addresses. It can be thought of like an index in a library that points to different racks of books – typically it serves as a reference to other more specific locations.
- – The top level domain server can be thought of as a specific rack of books in a library. This nameserver is the next step in the search for a specific IP address, and it hosts the last portion of a hostname .
- – This final nameserver can be thought of as a dictionary on a rack of books, in which a specific name can be translated into its definition. The authoritative nameserver is the last stop in the nameserver query. If the authoritative name server has access to the requested record, it will return the IP address for the requested hostname back to the DNS Recursor that made the initial request.
You May Like: Squarespace With Godaddy