What Is The Fqdn
Sometimes you will need to use the Fully Qualified Domain Name of your computer. It is a way of providing more context to the system. It is simply the hostname + suffix. For a PC with the hostname SSCSUPERCOMP the FQDN would be SSCSUPERCOMP.ads.ssc.wisc.edu.
At the SSCC, your suffix is typically *.ads.ssc.wisc.edu or *.ssc.wisc.edu. , depending on the system. The graphic below shows an analogy using a person’s name vs fullname and address:
How Do You Look Up A Fully Qualified Domain Name
Looking up the FQDN of your computer or server is simple. Just follow the instructions for your operating system below. If your machine does not provide the FQDN, it is not connected to a domain.
Windows 10. Within the taskbars Search Windows box, type control panel and select system and security. Next, select system and the FQDN is listed next to the Full Computer Name label.
Mac OS. Open terminal, and enter hostname -f into the prompt. Terminal will return the FQDN.
Linux. Open terminal and enter hostname -A into the prompt. The A is case sensitive. Terminal will return the FQDN.
Once you know your Fully Qualified Domain Name, you can make your device available online through the DNS.
The Parts Of A Domain
Computers interpret domains from right to left because the same domain name could be registered with multiple top-level domains . Therefore, reading right-to-left allows DNS resolution to be accurate and efficient.
Letâs take a closer look at the hierarchical structure of a domain: the protocol, the subdomain, the domain name, and the TLD.
You May Like: How To Make A Domain Name For Free
More Information On Fqdn
Fully qualified domain names actually require a period at the end. This means www.microsoft.com. would be the acceptable way to enter that FQDN. However, most systems simply imply the period even if you don’t explicitly give it. Some web browsers might even let you enter the period at the end of a URL, but it’s not required.
Domain names that aren’t “fully qualified” will always have some sort of ambiguity about them. For example, p301srv03 can’t be an FQDN because there are any number of domains that might also have a server by that name. p301srv03.wikipedia.comand p301srv03.microsoft.comare just two examplesknowing only the hostname doesn’t do much for you.
Even microsoft.com isn’t fully qualified because we don’t know for sure what the hostname is, even if most browsers do automatically assume it’s www.
These domain names that aren’t fully qualified are actually called partially qualified domain names. The next section has more information on PQDNs.
Examples Of A Fully Qualified Domain Name
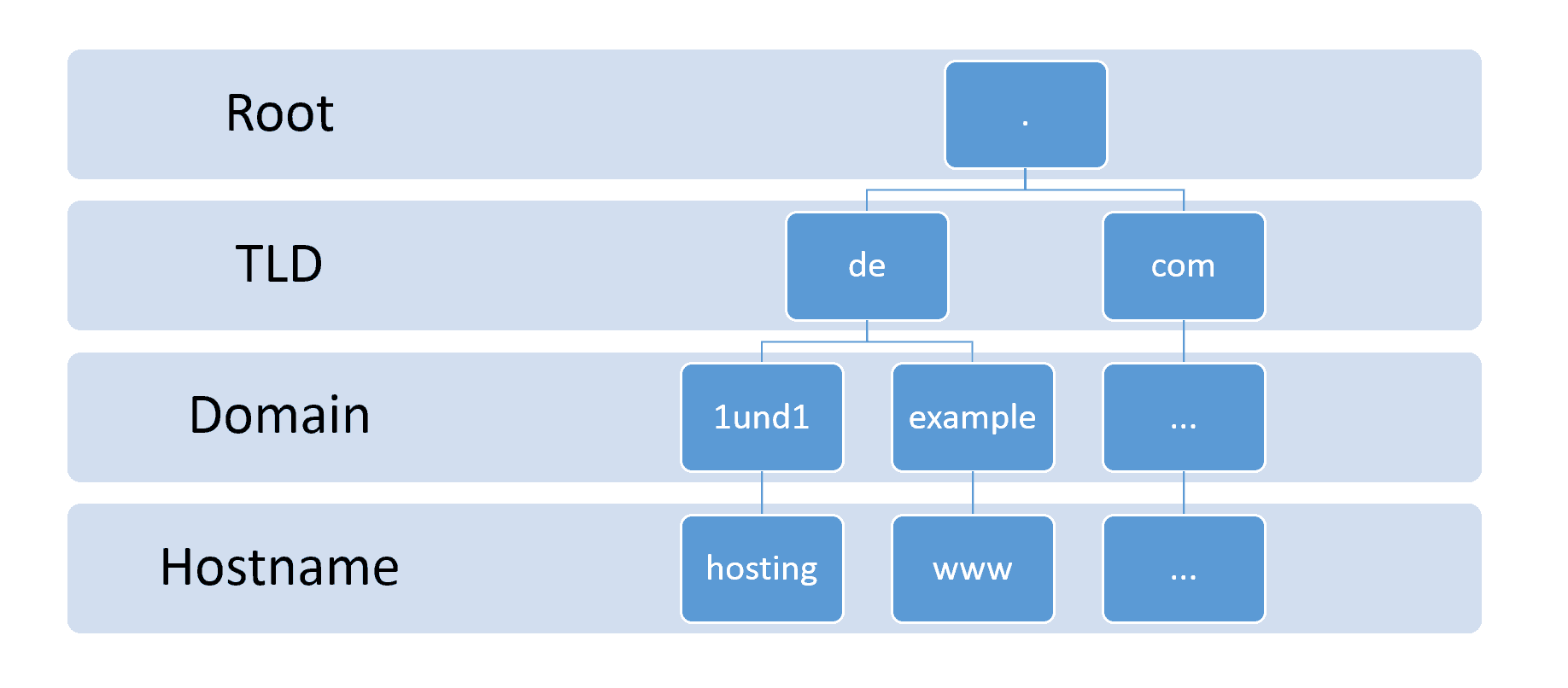
A fully qualified domain name is always written in a specific format.
If youre a Gmail user, then youve no doubt seen this one,mail.google.com.
Or, how about this one, en.wikipedia.org? In this case, the host name is en, which specifies the English version of the host.
Its funny, but most domain names arent technically fully qualified. For example, amazon.com isnt technically fully qualified because were not 100% sure of the host name, even though most browsers assume the host name is www.
Read Also: Where To Buy Email Domain
Fully Qualified Domain Name Example
A fully qualified domain name consists of a list of domain labels representing the hierarchy from the lowest relevant level in the DNS to the TLD. The domain labels are separated by the full stop . Character .
The fully qualified domain name always ends in the top-level domain due to the DNS root domain is unnamed which is expressed by having an empty label terminated by the dot in the DNS hierarchy.
That is most notable in DNS zone files in which a fully qualified domain name must be specified with a trailing dot. For example, moviemaker.minitool.com explicitly specifies an absolute domain name that ends with the empty top-level domain label. A device with the hostname moviemaker in the parent domain minitool.com has the FQDN moviemaker.minitool.com. the FQDN uniquely distinguishes the device from any other hosts called moviemaker in other domains.
Tip:
What Is A Partially Qualified Domain Name
Another term you might have come across is PQDN, or a Partially Qualified Domain Name. This is similar to a FQDN, but the domain isnt fully specified. Typically, this will refer to a portion of the domain name, but you wont have every detail to specify it completely.
This was mentioned briefly above in the example amazon.com. Although the web host will guess the www. aspect, it still isnt fully specified.
Typically, a PQDN is used for convenience in very specified contexts, like leaving out the www portion.
But, its important to understand that a FQDN and PQDN arent the same thing. With a FQDN you have the entire path of the host, but with a PQDN you only have a small-specified portion that works within a specific context, because the additional host details are contained within the system. Like a web browser intuiting the www portion of a web address.
Read Also: Can You Make Your Own Domain Extension
How Do You Find Your Fully Qualified Domain Name
Locating your FQDN address for your website is easy: just look at the address bar in your browser. Youre probably amazed at the frequency youve been interacting with Fully Qualified Domain Names, without even realizing it!
But, beyond a websites domain, both your computer and server have their own unique FQDN as well.
Heres how you locate your machines FQDN:
- For Mac users: Open up Terminal and type in hostname f. This will return your FQDN.
- For Windows users: You can find your FQDN within your system settings. First navigate to your Control Panel and locate System and Security. From here select System and youll find your FQDN listed on this screen.
The One And Only Fully Qualified Domain Name
A Fully Qualified Domain Name is the complete domain name of a specific computer, or host, online. An FQDN is comprised of several elements: a hostname and a domain name. These elements are separated by a period.
All FQDN follow the format .., where the domain might also include a subdomain. We read the FQDN from right, its root, to far left, its host.
Take www.GoDaddy.com, for example. The first element and domain level of the FQDN is the top level domain , which, in this case, is .com. Within the TLD, GoDaddy is the assigned domain name/second-level domain. Lastly, www. is the hostname.
A hostname often specifies a particular service or protocol for a domain such as mail or ftp in mail.domain.com or ftp.domain.net, respectively. Many websites today do not include www. in their URLS, and therefore are only partially qualified domain names.
Technically, FQDNs contain an empty element to the right of the TLD that signifies the unnamed domain root zone, and thus a trailing period follows the TLD . However, todays software usually processes the trailing period for us. The unnamed domain root zone essentially represents the internet.
A Fully Qualified Domain Name designates the specific location of an object within the Domain Name System hierarchy it communicates the hosts position relative to the root of the DNS namespace. An FQDN enables each entity connected to the internet to be uniquely identified and located within the internet framework.
Recommended Reading: Why Are Domain Names So Expensive
Fully Qualified Domain Name Faq
What is the maximum length for a fully qualified domain name, including the trailing period?How to find fully qualified domain name?
In Windows, go to Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Domains and Trusts. In the left panel, look under Active Directory Domains and Trusts and the FQDN for this computer is there.
Or, you can get your fully qualified domain name via command prompt.
What Is A Fully Qualified Domain Name
A fully qualified domain name gives its precise location in the hierarchy of DNS records. It is the complete address for websites and other computers and entities accessing the Internet resolving to the root domain.
Using a Secure Sockets Layer certificate helps secure your domain. An SSL certificate offers a secured connection via HTTPS, providing encryption and authentication for your web addresses.
Letâs deal with the parts of a domain, which will help us better understand what an FQDN is.
Don’t Miss: Do You Need A Domain Name
Fqdn = Host Name + Domain Name
Now we came to the real topic. We have learned the basics which creates FQDN. Fully qualified means the whole and domain name cames after that. Fully qualified domain name consist of Host name + Domain name . FQDN specifies the host whit out any extra description. For example:
Hostname:www
www.poftut.com specifies the host which provides www or web services.
About Fully Qualified Domain Names
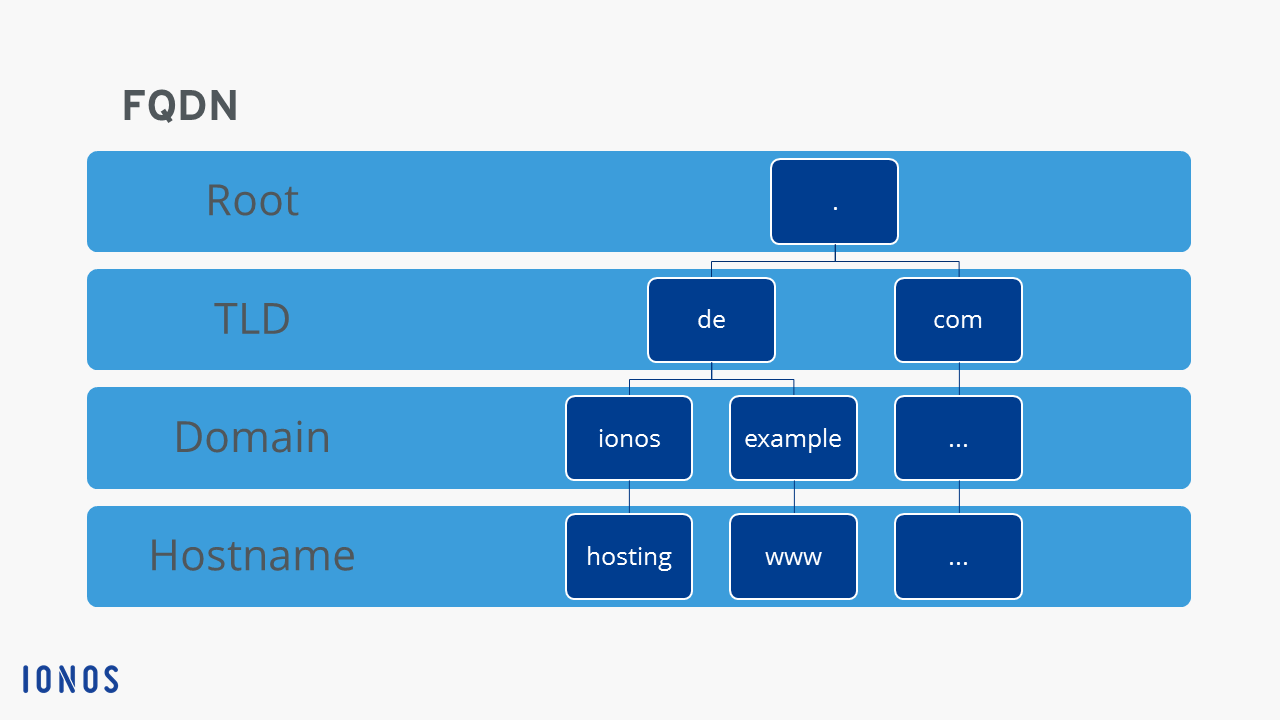
A fully qualified domain name is the complete domain name for a specific computer, or host, on the internet. The FQDN consists of two parts: the hostname and the domain name. For example, an FQDN for a hypothetical mail server might bemymail.somecollege.edu. The hostname ismymail, and the host is located within the domainsomecollege.edu.
In this example, .edu is the top-level domain . This is similar to the root directory on a typical workstation, where all other directories originate.
The same applies to web addresses. For example,www.indiana.edu is the FQDN on the web for IU. In this case, www is the name of the host in theindiana.edu domain.
When connecting to a host , you must specify the FQDN. The DNS server then resolves the hostname to its IP address by looking at its DNS table. The host is contacted and you receive a login prompt.
If you are using only the hostname to connect to a server, the application you’re using may not be able to resolve the hostname. This can happen if either the DNS suffix search order in your computer’s TCP/IP properties is incorrect, or the DNS table is corrupted. In these cases, entering the host’s FQDN will allow DNS to locate the server. Also, if you are trying to connect to a remote host that is not local to yourinternet service provider , you will probably have to use the FQDN. For example, it’s unlikely that a DNS server at IU would have a listing for remote hosts at another university or an unrelated ISP.
Read Also: How Do I Link My Domain Name To My Website
Fully Qualified Domain Name
A fully qualified domain name , sometimes also referred to as an absolute domain name, is a domain name that specifies its exact location in the tree hierarchy of the Domain Name System . It specifies all domain levels, including the top-level domain and the root zone. A fully qualified domain name is distinguished by its lack of ambiguity: it can be interpreted only in one way. It usually consists of a host name and at least one higher-level domain separated by the symbol “.” and always ends in the top-level domain.
The DNS root domain is unnamed which is expressed by having an empty label in the DNS hierarchy, resulting in a fully qualified domain name ending with the top-level domain. However, in some cases the full stop character is required at the end of the fully qualified domain name.
In contrast to a domain name that is fully specified, a domain name that does not include the full path of labels up to the DNS root is often called a partially qualified domain name.
How Are Fully Qualified Domain Names Used
If you want to make a website, computer, or any device accessible via an Internet network, then youre going to need an FQDN. However, youll also need to interface with the DNS records, so the location of that device, or website, can be found.
FQDNs are one of the most essential components of how the Internet and domains are organized. For that reason they have a wide variety of applications, that extend beyond letting your website or device be available to the Internet.
But, beyond that one of the most common reasons youll need to know your FQDN is for obtaining an SSL certificate.
Today, especially , an SSL certificate is becoming a necessity. To actually obtain an SSL certificate and secure your site youre going to need a Fully Qualified Domain Name.
Also, if youre connecting to your host remotely, then youll most likely need your FQDN to remotely connect. For example, if youre connecting over FTP then youll need the FQDN or the IP address to access the server.
You May Like: How Much Does Com Domain Cost
Structure Of The Fqdn
If you want to better understand the naming hierarchy of the FQDN, then it makes sense to look at the structure of an FQDN from right to left. The further right a label is located, the higher it lies in the tree diagram representation of the hierarchy. On the highest hierarchical level youll find the root label, also called the null label, or the root of the DNS system. It consists of a blank area, and so is only expressed by a period, or dot. In browsers today, its not necessary to enter this dot anymore, since the browser will add it itself.
On the next highest hierarchy level is the top level domain, for example .com, .org, or .ca. To resolve the address, the name server searches through the directory of the given TLD for the domain on the next hierarchy level. Once this is identified, the host whose host name is listed in the lowest label is contacted to access the given site.
Hostname And Domain Name
The domain and TLD comprise the domain name, while the hostname specifies different services and protocols for the domain. For example, “mail.example.com” is often the required format when configuring the SMTP server for an email account. The server address “ftp.example.com” is commonly used when connecting to an FTP server. Name servers typically use the naming convention “ns1.example.com” and “ns2.example.com”.
The hostname may also specify a website subdomain. The most popular subdomain is “www.” Other common subdomains include “support,” “dev,” “store,” and “forum.” Some sites use variations of “www” such as “web”, “ww1,” “www2,” etc.
Also Check: How To Change Domain Name Of Website
What Is The Difference Between A Domain Name And A Fully Qualified Domain Name
A fully qualified domain name contains both a host name and a domain name. For a landing page, the fully qualified domain name usually represents the full URL or a major portion of the top-level address. In looking at a fully qualified domain name, the host name typically comes before the domain name.
Look Up The Fqdn In Windows
In Windows, you can find the FQDN of your computer under the label Full computer name. To identify this in Windows 10, simply enter the term Control panel in the Windows search bar. Click on System and security and then on System. In the second to last section of this page, youll find the full computer name of your device, which consists of the specified computer name and the domain. If the computer isnt connected with a domain, then only the local host name will be displayed. In Windows 7, you can access this display by right-clicking on Computer in the start menu and then selecting Properties.
You can also display the FQDN over the command line in Windows. To do this, enter the following line and press enter:
echo %COMPUTERNAME%.%USERDNSDOMAIN%
This will then display your FQDN. If your computer isnt connected with a domain, then only the unmodified variable %USERDNSDOMAIN% will be displayed after the computer name.
Don’t Miss: How To Setup Email On Godaddy Domain