Contact Our California Eminent Domain Lawyers Today
Are you a property or business owner in Southern California who is being threatened by eminent domain? If so, then you require the expertise of a California eminent domain lawyer to help you fight for the just compensation you deserve. Palmieri, Hennessey & Leifer LLP in Irvine is one of the premier eminent domain law firms in all of California and specializes in eminent domain litigation and related real estate and land-use matters. We strongly encourage you to schedule a free consultation with one of our highly experienced California eminent domain lawyers and begin exploring your legal options. You may either submit your information through this online form or call Palmieri, Hennessey & Leifer at 949-851-7388.
Legal Definition Of Eminent Domain
: condemnexpropriatetakesense 1b
Note: The Fifth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution requires the government to compensate the owner of property taken by eminent domain, stating nor shall private property be taken for public use, without just compensation. State constitutions contain similar provisions requiring that the property owner receive just compensation for the property taken.
More from Merriam-Webster on eminent domain
Contesting The Condemning Agency’s Acquisition Of The Property
Provided there has been no withdrawal of the amount deposited, anyone with an interest in the property can challenge in court the agency’s right to acquire or condemn the property. However the right to challenge the acquisition must have been preserved at the hearing on the Resolution of Necessity.
The agencys right to acquire the property by eminent domain will be decided by the judge, not a jury.
Recommended Reading: How To Link Website To Domain Name
How Do I Protect My Property From Eminent Domain
Unfortunately, there is not much you can do to protect your property from eminent domain. It is not always real estate that is seized, and it is not possible to anticipate the future needs of the public or the government. It may seem unfair, but property owners do not have many options to protect their property from seizure by the government.
Eminent Domain And Federal Law
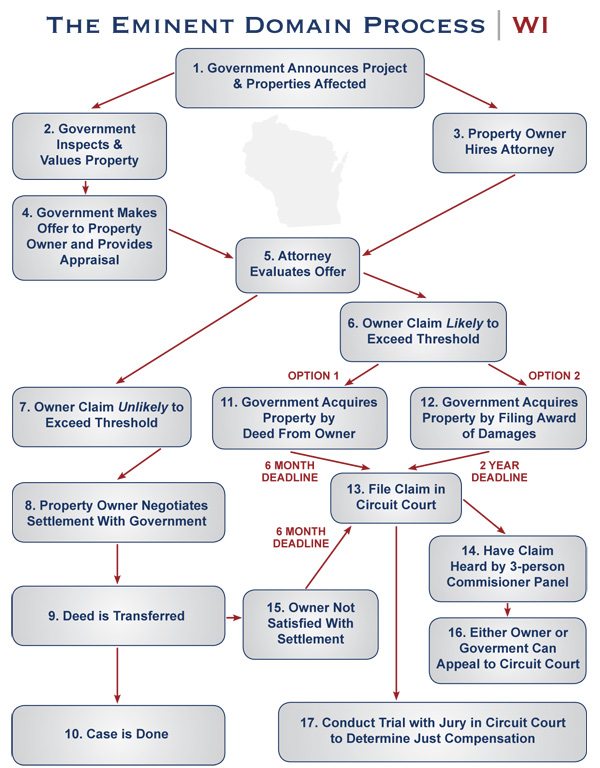
The law of eminent domain originates in the “Takings Clause” of the Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The U.S. Supreme Court helps decide major cases regarding eminent domain.
The framers of the Constitution were generally wealthy landowners who wanted certain guarantees against tyranny. However, they understood that sometimes land would have to be taken for the public good.
The Takings Clause states that “private property be taken for public use without just compensation.” This only applies to private property and must be used for the public good.
Interstate highways, to use a common example, typically are considered public goods.
You May Like: How To Migrate Users From One Domain To Another
Has Anyone Ever Won An Eminent Domain Case
Many people have won eminent domain cases in the sense that their fair market value claim was awarded. The claimant, in this case, would be an aggrieved property owner who can sue for a higher value than what the government assessed, although these cases are lengthy and extremely expensive to pursue. Most private property owners find it is easier to just accept the value and move on with their lives. It is nearly impossible to halt an eminent domain case, although it is possible to pursue further compensation.
What Are The Phases Of Eminent Domain
Eminent domain cases have two phases: 1) the right to take phase is the first one, and 2) the just compensation, or damages, phase is the second one. Everything discussed in this overview up to this point has addressed the first phase. In cases where the condemning authority initiates the taking, the first phase involves determining whether the condemning authoritys project satisfies the public use/purpose requirement. In an inverse condemnation case, the first phase involves determining whether a taking actually occurred. In all eminent domain cases the second phase does not begin until the first phase is completed.
You May Like: Is My Domain Email Blacklisted
How Eminent Domain Works In Real Estate
If you own property, how might eminent domain impact you? What steps will a government take if it wants to claim your property for a public project?
Theres a process to eminent domain. The government wont show up and say theyre taking your land tomorrow. Instead, they must follow a series of steps.
Lets say the government wants to expand a highway to relieve traffic congestion. To make that plan work, it needs to purchase your residence and demolish it.
What usually happens is that the governmental authority that wants your land will offer to buy your property at a specific price. If you accept the offer, the sale goes forward and you can use the proceeds to find a new place to live. If you dont like the offer, you can negotiate for more money.
If you dont wish to sell under any circumstance or cant come to an agreement on a price, these differences are resolved in a condemnation proceeding.
What Is Compulsory Acquisition
Compulsory acquisition is another term for eminent domain. It can be enacted by all levels of government, from federal right through to local. Public works like widening roads, infrastructure projects, and improving public safety are typical reasons behind these government land acquisitions. Compulsory acquisitions are relatively common in rural areas, mainly because there is less infrastructure.
Don’t Miss: How To Buy A Website Domain For Free
I Am A Real Estate Professional What Does This Mean For My Business
Used carefully and judiciously, the power of eminent domain can help communities invest in projects that are necessary for them to function effectively, such as roads, bridges and water management systems. These kinds of projects help preserve property values and create the conditions for robust economic growth.
Improper or incorrect use of eminent domain can harm property rights and destroy trust in public institutions.
What Is Eminent Domain A Lawyers Eminent Domain Definition
Eminent Domain refers to the right that the state, or someone authorized by the state, has to take private property for public use.
There are four elements to Eminent Domain that are crucial: that it is private property, that it was taken in some way, that it was taken for a public use, and that there was just compensation for that taking.
Property does not just refer to land but also may refer to water, air or even partial property, which could be if the value of a property has been diminished by other government action. For example, if a property has been changed from being waterfront to no longer being waterfront by the government filling in a pond or stream, that would diminish the value of the property and would be a partial property taking.
The government takes private property through condemnation proceedings. This is not the same as a property being condemned and does not indicate that there is anything wrong with the property.
Condemnation proceedings generally occur within the court system when the property owner does not agree that the government has the right to take the property or when the property owner does not agree on the suggested compensation for that property.
Also Check: What Is Web Hosting And Domain
Disputes In Eminent Domain
One should not conclude, though, that there are very few disputes in eminent domain cases. To the contrary, there are a lot of them. Those disputes, however, are over the amount of money which should be paid for the property being taken by the condemning authority. That is what the second phase of an eminent domain case is all about.
The purpose of this introductory overview is to provide the reader with a roadmap to understand how eminent domain works. This website is designed to allow the reader to explore these eminent domain issues in greater detail. Since just compensation issues are so vast, we wont even attempt to address them in this overview. But they are covered extensively in the website, and you are invited to explore them at your leisure.
Even after reading and contemplating the information in this website, many readers are likely to still have unanswered questions. For that reason, we invite those readers to contact us directly with their questions. This is particularly pertinent for those readers who are actually facing a potential taking. Talking to a skilled eminent domain lawyer is the only way to make sure your questions are answered. To encourage readers with potential cases to understand their cases better, we will talk about your case with you, and even analyze it, at no charge.
Learn more by reading our Frequently Asked Questions for Eminent Domain.
The Owner And The Agency Are Unable To Reach An Agreement On The Property’s Fair Market Value
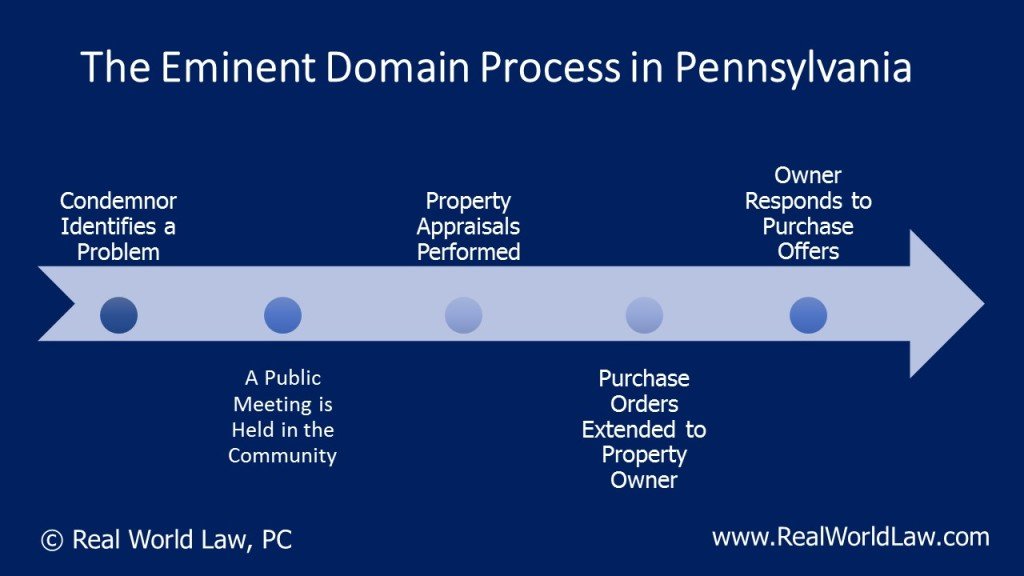
The agency, to the greatest extent practicable, should make every reasonable effort to acquire the property by negotiated purchase. If the negotiations are unsuccessful, the agency may either file an eminent domain action in a court located within the same county where the property is located or it may decide to abandon its intention to acquire the property. If the agency abandons its intention to acquire, it must promptly notify the owner.
If the agency proceeds with eminent domain, the first step is for agency staff to request authority from the legislative body to file a condemnation action. The approval from the legislative body is called a “Resolution of Necessity.” In considering whether condemnation is necessary , the legislative body must determine:
- Whether the public interest and necessity require the project
- Whether the project is planned or located in the manner that will be most compatible with the greatest public good and the least private injury
- Whether the property is necessary for the project and
- Whether an appropriate offer with supporting data was provided to the owner.
Recommended Reading: How To Setup Email On Godaddy Domain
The Eminent Domain Trial
Typically, the purpose of an eminent domain trial is to determine the fair market value of the property, including compensable interests such as lost business goodwill caused by the taking or severance damages. The trial is usually conducted before a judge and jury. Anyone with an interest in the property and the agency will have the opportunity to present evidence of value, and the jury will determine the property’s fair market value. In cases where the parties choose not to have a jury, the judge will decide the property’s fair market value. Value testimony is almost universally presented by expert testimony. Generally, each party to the litigation must disclose its respective appraisals to the other parties prior to trial.
If the owner challenges the agency’s right to acquire the property, the eminent domain trial will also determine whether or not the agency has the legal right to acquire the property. In such cases, the judge will make this determination before any evidence is presented concerning the property’s fair market value.
At the end of the trial, the judge will enter a judgment requiring the agency to pay fair market value. Once the agency pays the amount listed in the judgment, the judge will enter a final order of condemnation. The agency will record the final order with the County Recorder, and title to the property will then pass to the agency.
How Does Eminent Domain Work
Eminent domain power permits a federal, state, and local authority to identify, acquire, and convert a property for public use or purpose on meeting certain conditions. Its origin dates back to Magna Carta. It was a royal charter of rights signed by King John of England and rebel barons in 1215. It was when kings seized properties owned by barons and compensated them in exchange for taking.
The government estimates the market value of the property before offering just compensation to possess it. If the property owner does not think the amount is fair or questions the legality of the possession, the court will hear the matter. However, these legal disputes are costlier and time-consuming, as per the U.S. Department of Home Security report of 2009.
According to the Fifth Amendment of the United States Constitution, eminent domain in real estate works on two basic principles:
- The owner must receive just compensation in exchange for taking.
The eminent domain law addresses conflicts between individual interests and public needs. According to the condemnation jurisprudence, if the property owner refuses to sell their property despite the fair compensation, the government can take its possession without their consent. The law also states that an individual should not have the right to stop the task planned for public welfare.
Read Also: How To Tell Who Owns A Website Domain
Examples Of Eminent Domain In A Sentence
eminent domaineminent domain San Diego Union-Tribuneeminent domain The Indianapolis Stareminent domain Arkansas Onlineeminent domain Chroneminent domain Los Angeles Timeseminent domain Los Angeles Timeseminent domainNBC Newseminent domain The Salt Lake Tribune
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ’eminent domain.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Oppose The Motion For An Order For Possession Prior To Judgment
Owners and tenants may oppose the motion in writing by serving the agency and the court with written opposition within the period of time set forth in the notice from the agency. In ruling on a prejudgment possession order the court must balance the hardship to the owner or tenant against the hardship to the agency.
Don’t Miss: How To Renew My Domain Name With Godaddy
Elements Of Eminent Domain
To exercise the power of eminent domain, the government must prove that the four elements set forth in the Fifth Amendment are present: private property must be taken for public use and with just compensation. These elements have been interpreted broadly.
Private Property The first element requires that the property taken be private. Private property includes land as well as fixtures, leases, options, stocks, and other items. The rifle that was used to kill President john f. kennedy was considered private property in an eminent domain proceeding.
Taking The second element refers to the taking of physical property, or a portion thereof, as well as the taking of property by reducing its value. Property value may be reduced because of noise, accessibility problems, or other agents. Dirt, timber, or rock appropriated from an individual’s land for the construction of a highway is taken property for which the owner is entitled to compensation. In general, compensation must be paid when a restriction on the use of property is so extensive that it is tantamount to confiscation of the property.
Some property rights routinely receive constitutional protection, such as Water Rights. For example, if land is changed from waterfront to inland property by the construction of a highway on the shoreline, the owners of the affected property are to be compensated for their loss of use of the waterfront.
Hawaii Housing Authority V Midkiff
The central holding of Berman was reaffirmed in this 1984 Supreme Court decision. Hawaii had decided to break up a land oligopoly that grew out of the states precolonial property system. Using its eminent domain power, the Hawaii legislature redistributed much of this land to a greater number of people, arguing that it was in the public interest. The Supreme Court called this a valid public use and emphasized that it would largely defer to legislative determinations on the subject.Kelo v. City of New LondonThe 2005 Kelo case arose out of a municipal revitalization plan that called for transferring private property to a private economic development corporation. Ruling in favor of New London, the Court called the citys objective a valid public use as it had a rational basis to believe that approximately 1,000 new jobs would be created through the plan.
Recommended Reading: How Much To Offer For A Domain Name
Why Is Eminent Domain In The Fifth Amendment
Eminent domain is in the Fifth Amendment to ensure that the U.S. government is able to acquire assets that benefit the public good. An example of this would be if a town needed water, and the only possible way to bring water to that town was through the property of a private landowner. The landowner may not want pipes running through their property, but since it benefits the public, the government will pursue it.
What Should A Homeowner Do When He Or She Receives Notice

It is important that a homeowner does not ignore the notice he or she receives. It should be taken seriously. Homeowners should contact an attorney to look over the paperwork and explain exactly what is happening. The attorney should also look over the intended use to ensure it is fair. In addition, a proper appraisal should be done to ensure the compensation is indeed adequate for the property being taken.
Also Check: How Much Is It To Purchase A Domain Name
The History Of Eminent Domain
Eminent domain has a fairly simple definition: the power of government to take property from private individuals, businesses, and non-governmental entities. The taking of property is known in some states as an acquisition, while eminent domain is frequently called condemnation. Although it is sometimes thought that this concept originated with the founding of our country, it actually has existed long before that. Historically, the power of eminent domain was exercised by the ruling class, or royalty, which was known as the sovereign or sovereignty.
The innovation to the power of eminent domain, which was produced by the founding of the United States, was the creation of two conditions upon the exercise of that power. These are found in the 5th Amendment to the Constitution. The first requires that the taking must be for a public use. The second condition requires that just compensation be paid to the former owner in an amount equal to value of the property taken. While the federal constitution only applies to the taking of property, many state constitutions expanded owner rights by requiring the payment of just compensation for damage to property, as well.
Loans On/against The Property
Where the agency is acquiring the entire property, generally the compensation payable to the owner is first used to satisfy outstanding loans or liens as in a typical real estate transaction. Where less than the entire property is being acquired, whether outstanding loans or liens are paid from the compensation will depend on the particular facts and circumstances.
Also Check: What Is Dell Emc Data Domain