Common Characteristics Of Workgroup Accounts In Windows 10
- No computers in the workgroup has control over any other computer rather, they are peer computers
- Each computer in the workgroup has multiple accounts associated with it. Each workgroup account can only log into the workgroup computer it belongs to
- Workgroup accounts are not password-protected
- Computers in a workgroup must all be on the same LAN or subnet
- The number of computers in a workgroup is far smaller than in a domain. This breaks down to an average of 20 computers for a workgroup
What Is Active Directory
Microsoft introduced Active Directory for centralized domain management in Windows Server 2000. But later in the 2008 Windows Server, Active Directory also included other services such as Directory Federation Services for Single Sign-On, security certificates for public key cryptography, rights management and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol .
Essentially, an Active Directory is a framework for managing several Windows Server domains, while a domain controller is a critical part of the Active Directory. It is the server that runs the Active Directory and authenticates users based on the data stored in the Active Directory.
An Active Directory stores information as objects, which are organized into forests, trees and domains. Each AD forest can have multiple domains, and domain controllers manage trusts between those domains to grant users from one domain access to another domain. There are several types of trusts that exist between domains:
System administrators can also set security policies, such as password complexity, through domain controllers.
What Is A Domain Controller And Why Would I Need It
User authentication and authorization is critical for protecting your network infrastructure. It ensures that only trustworthy and relevant users can access the network. A Windows Server domain logically groups users, PCs and other objects in a network, while a domain controller authenticates access requests to the domains resources. It also stores information about user accounts and devices, and it enforces security policies.
Learn the important role of a domain controller within a network infrastructure, and set it up with fault tolerance.
Also Check: How Much To Buy A Domain Name
Which Account Type Should You Choose
Domain and workgroup accounts are different accounts, but they both have their own distinct uses. Domain accounts should be set up when an organization is larger than 20 computers , with resources large enough to have at least one domain controller server .
This account type is best suited to organizations where users have different privilege levels and where there is a need for at least some control of network resources. If your organization is an enterprise, school or other large organization, this is the account for you.
Workgroup accounts are best suited to home computers, small networks where all users have the same privileges, and for networks that do not have a domain controller server. The easiest part about the workgroup account is that you do not have to join it you are part of the workgroup club right out of the box.
Prerequisites For Windows 11 Domain Join
If you are planning to add or join Windows 11 computer to AD domain, here are the basic requirements.
Recommended Reading: How To Find Out Who Owns Domains
What Server Types Are Used In A Dns Check
There are 4 different types of DNS servers involved when performing a DNS check. Each has a different role and may not be needed at all depending on the situation, having all these different server types is what contributes to DNS propagation issues.
Recursive Resolver – The DNS server your device communicates with is called the recursive resolver and is issued to you automatically by your ISP, but can be also configured on your router or individual devices. These DNS severs are ideally located in close geographical proximity to return results as fast as possible. These servers will cache a copy of the DNS results to speed up future DNS lookup requests.
Root Name Server – This type of DNS server is responsible for returning the IP address of the TLD nameserver. For instance, if it is trying to resolve example.com, the root name server returns the IP of the TLD name server that runs .com domains.
TLD Name Server – This name server returns the authoritative name servers for each domain under the Top Level Domain it’s responsible for. The .com TLD name server will return results for example.com but not example.org.
– This stores DNS servers’ configuration data for specific domain names.
How Do I Login As A Domain User
To log on to this computer using an account from a domain other than the default domain, include the domain name in the user name box using this syntax: domainusername. To log on to this computer using a local user account, precede your local user name with a period and backslash, like this: . username.
Don’t Miss: How To Determine Who Owns A Domain
How Can Cloud Directory Services Help
Previously, IT infrastructure was largely Microsoft-based, so companies relied entirely on Microsofts Active Directory for access management. But now, as IT networks are increasingly shifting to the cloud, cloud-based access management options have also emerged. Cloud directory services are a modem alternative to the traditional, on-premises Active Directory. Delivered through the cloud, these services can be used to build an identity management system from scratch or extend your companys Active Directory services across cloud and on-premises environments.
Cloud directory services provide similar functionality to Microsoft Active Directory services along with the added security, scalability and convenience of the cloud. For companies running on a single domain controller, cloud directory services, such as Azure Directory, make it extremely simple and quick to set up a secondary domain controller in the cloud. With a secondary domain controller within the Azure cloud, your Network infrastructure can enjoy business continuity and resilience at a very low cost.
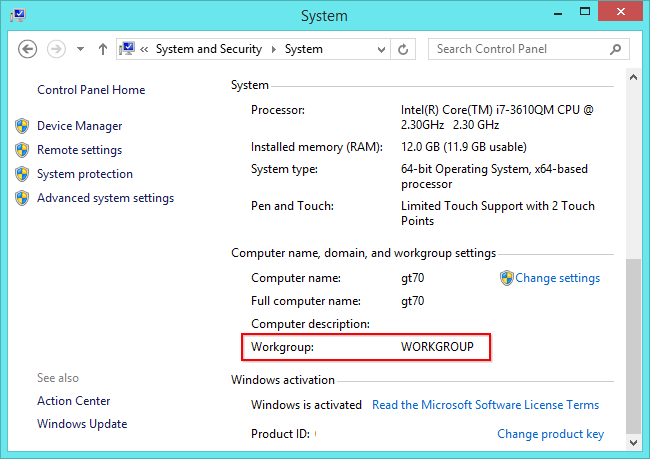
What Is The Difference Between A Workgroup And A Domain
The main difference between workgroups and domains is how resources on the network are managed. Computers on home networks are usually part of a workgroup, and computers on workplace networks are usually part of a domain. To use any computer in the workgroup, you must have an account on that computer.
You May Like: How To Transfer Squarespace Domain To Shopify
What Is Domain Name And Ip Address
In short, an IP address is the address that computers, servers and other devices use to identify one another online. The vast majority of IP addresses are arranged into four sets of digits i.e., 12.34. 56.78. A domain name is the information that you enter into a web browser in order to reach a specific website.
Look Up Your Computer’s Domain Name
To find the Domain for your computer:
For Windows machines, click on the Start Menu, go to Control Panel, System and Security, then System.
You’ll see your computer’s domain name at the bottom.
For any additional questions or concerns regarding proximity settings, computer locking, credential management, or compliance, please contact GateKeeper Enterprise support using the Support Ticket form on or email .
—————————————————————————————————————————————GateKeeper domain address computer domain name computer username computer user name username for computer domain for computer whoami command which computer domain is this domain name of this computer? how to find out the domain name of this computer? domain name of my computer? find my domain name for my PC laptop domain name desktop domain name
You May Like: What To Do After Buying Domain
What Is Trace Command In Cmd
The tracert command is a Command Prompt command that’s used to show several details about the path that a packet takes from the computer or device you’re on to whatever destination you specify. You might also sometimes see the tracert command referred to as the trace route command or traceroute command.
What Is A Domain Name
New computer users often confuse domain names with universal resource locators, or URLs, and Internet Protocol, or IP, addresses. This confusion is understandable. It is worth learning the differences between them because these terms are ubiquitous. It is also helpful to be able to use terms correctly when communicating to technicians or other people within a professional organization.
This naming convention is analogous to a physical address system. People find web pages in a manner similar to the way that they use maps to find physical locations. If the Internet is like a phone book, and a web page is like a physical building, the URL would be the precise street address of that building. The IP address would be like the car that travels to its destination. There are also other useful metaphors for understanding this relationship.
You May Like: What Is The .io Domain
Why Should I Have A Secondary Domain Controller
A domain controller authenticates and authorizes users, which is a primary security function in a network infrastructure. It has all the keys to the realm of your Windows Server domain. Now, if your domain controller goes down, there will be no way for your users to authenticate themselves and access any of the domains resources. All applications, services and even business-critical systems that require Active Directory authentication will be inaccessible. Automatic designation of Internet Protocol addresses will fail, forcing system administrators to revert to manual assignments.
You may even have to rebuild your entire server from scratch, which could take days and even weeks if your company does not have an established backup protocol. This is why resilience is so important for ensuring business continuity and minimal or no downtime. Investing in a secondary domain controller can reduce downtime considerably in the event of domain controller failure. While your IT team works to restore the failed domain controller, a secondary domain controller will ensure that your users are able to access important domain resources and that business-critical systems and services keep running until everything goes back to normal.
How Do You Speed Up Dns Propagation
A technique used to speed up DNS propagation and prevent a delay is to lower your DNS records TTL a few days in advance of making any changes so that when the change is made any old records expire more quickly. Unfortunately, most people who are having issues and trying to speed up DNS propagation only find this out after making changes and are wondering why they’re not seeing instant results.
If you have checked DNS globally, and are seeing different results locally then you may consider flushing your DNS cache, or using another DNS server. As a last resort, manually overriding your local DNS entries in your systems hosts file can also be done but should be considered a temporary measure and only works for certain record types.
Recommended Reading: How Much For A Domain Name Per Year
What Are Workgroup Accounts
Workgroup accounts are the default account for Windows 10 computers and belong to the most basic of network infrastructures. This means that unless you join a domain , your account will remain in a workgroup.
Unlike domains, workgroups are not managed by a domain controller server. Rather, no computers in the workgroup have control over the others.
This type of account is suitable for home, small business, and clusters of computers that reside on the same local area network . The biggest benefit for the user with workgroup accounts is that users can make changes with local group policy that would be impossible in a domain without administrator credentials.
Domain Names And Urls
The universal resource locator, or URL, is an entire set of directions, and it contains extremely detailed information. The domain name is one of the pieces inside of a URL. It is also the most easily recognized part of the entire address. When computer users type a web address directly into the field at the top of their browser window, it initiates a process of locating the page requested. To do so, the instructions contained inside the URL, including the domain name, must correctly point to that location. The IP address is a numerical code that makes this possible.
Recommended Reading: How To Transfer Godaddy Domain To Shopify
Other Domain Name Types
We focused on the different extension types above. The following are the different available structures of domain names:
Second-Level Domains
Second-level domains are below TLDs in the domain name hierarchy. An SLD is the section of a domain name located on the left side of the last dot. Take www.hostinger.com, for example hostinger is the SLD, and .com is the TLD.
Some domain name registries use an SLD to indicate a specific type of entity registering. For example, academic institutions in the United Kingdom mostly register websites under .ac.uk.
Subdomains
A subdomain is a separate division from a larger domain but still shares the same servers. There is no need to purchase and register a subdomain. Technically, the www on most URLs is a subdomain that indicates a site is part of the world wide web.
The most common use for a subdomain is to organize and divide web content into separate sections. For example, Google uses developers.google.com to provide specific information for developers.
Another use of a subdomain is to create another website with the same name but different languages. Take Wikipedia as an example, which has a separate subdomain for each language. It uses en.wikipedia.org for the English version and es.wikipedia.org for the Spanish one.
Free Domains
A free web address often uses the same structure as subdomains. For example, instead of hostingertutorials.com, it would be hostingertutorials.wordpress.com or hostingertutorials.blogspot.com.
Gtlds: Generic Top Level Domains
A generic top-level domain is an extension that does not rely on a country code. There are no specific criteria to get a gTLD. However, some extensions are sponsored by designated agencies or organizations.
Some generic TLDs are restricted to specific types of registrants. For example, an academic institution can use .edu, and a governmental agency can use .gov. If your domain does not fall under particular categories or institutions, you will not be able to use the extension.
Recommended Reading: Shopify Transferring Domain
What Are Domain Accounts
Domain accounts are likely the type of account you are thinking of when you think of those used in organizations and enterprise in general. In fact, domain accounts were designed for the purpose of managing networks and resources on workplace networks. This type of account is the most tightly controlled of all Windows 10 accounts and is managed by a network administrator.