What Is An Authoritative Dns Server
An authoritative DNS server holds and maintains DNS records. It is the last server in a DNS lookup chain that responds with the queried DNS record. An authoritative DNS ultimately allows a web browser with the URL request to reach the IP address needed to access a website or other web resources. An authoritative DNS domain name server is a definitive source for DNS domain name resolution.
DNS security technology is used to protect DNS information stored as a record in the Domain Name System . It provides secure authentication for the origin of the DNS data, helping to safeguard against attacks and protect data integrity.
What Is A Domain Name Domains Explained For Beginners
A domain name is essentially your websites equivalent of a physical address. In the same way that a GPS needs a street address or a zipcode to provide directions, a web browser needs a domain name to direct you to a website.
A domain name takes the form of two main elements. For example, the domain name Facebook.com consists of the websites name and the domain name extension . When a company purchases a domain name, theyre able to specify which server the domain name points to.
Domain name registrations are overseen by an organization called ICANN . ICANN specifies which domain name extensions are available and keeps a centralized database of where the domain names point to.
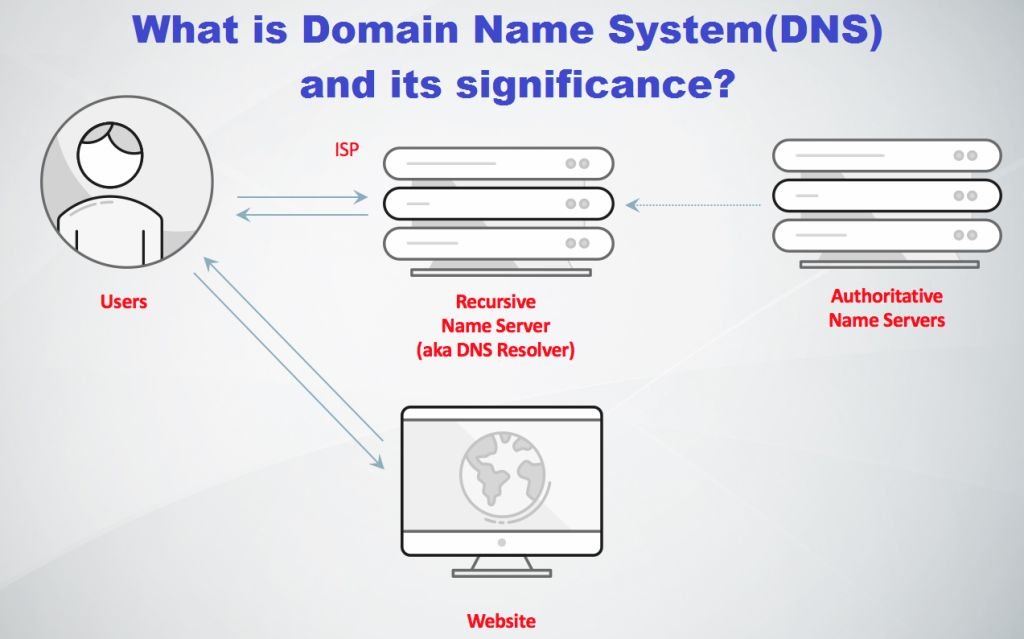
Every website that you visit effectively consists of two main elements: a domain name and a web server.
How Does Dns Work
The process of DNS resolution involves converting a hostname into a computer-friendly IP address . An IP address is given to each device on the Internet, and that address is necessary to find the appropriate Internet device – like a street address is used to find a particular home. When a user wants to load a webpage, a translation must occur between what a user types into their web browser and the machine-friendly address necessary to locate the example.com webpage.
In order to understand the process behind the DNS resolution, its important to learn about the different hardware components a DNS query must pass between. For the web browser, the DNS lookup occurs “behind the scenes” and requires no interaction from the users computer apart from the initial request.
Recommended Reading: How To Get A Business Domain Email
What Is A Dns Resolver
The DNS resolver is the first stop in the DNS lookup, and it is responsible for dealing with the client that made the initial request. The resolver starts the sequence of queries that ultimately leads to a URL being translated into the necessary IP address.
Note: A typical uncached DNS lookup will involve both recursive and iterative queries.
It’s important to differentiate between a query and a recursive DNS resolver. The query refers to the request made to a DNS resolver requiring the resolution of the query. A DNS recursive resolver is the computer that accepts a recursive query and processes the response by making the necessary requests.
What Is Split Dns
If you are in a corporate environment and you have a web server that you list as www.yourwebsite.com with a public DNS record of 74.125.227.210 but you are inside your network and your firewall will not allow traffic to go out and make a u-turn and come back in, you will not be able to get to the website. How do you resolve this for your internal clients? You make a split DNS. This means that there is a public DNS zone for yourwebsite.com that contains an A Record for www that resolves to 74.125.227.210 and you have an internal DNS zone that also has a zone for yourwebsite.com, but it has an A Record for www that resolves to 10.1.2.3 . Now your client that is on the inside of your corporate network can communicate with your web server at www.yourwebsite.com. If this is a mobile device, you could move between networks and still have access to the website. Of course with this split DNS zone, you will have to enter every record that is in the public DNS zone or you will break the other records while on the internal network.
Another split DNS zone implementation is to do it just for the record you wish to redirect. You would create a DNS zone for www.yourwebsite.com and have the default record resolve to 10.1.2.3. This way, you only have to maintain one record internally, instead of every record that is in the public DNS zone.
You May Like: 866-731-6556
Cctld: Country Code Top Level Domains
ccTLDs use just two letters and are based upon international country codes, such as .us for the United States and .jp for Japan. Theyre often used by companies that are building dedicated sites for specific regions and can be a good way of signaling to users that theyve arrived at the right place.
Whats In A Domain Name
Domain names function on the Internet in a manner similar to a physical address in the physical world. Each part of the domain name provides specific information. These pieces of information enable web browsers to locate the web page. The naming system is closely regulated in order to prevent confusion or duplicate addresses. As demand increased exponentially, a new Internet Protocol version, or IPv6, was created to expand the number of domain names available.
You May Like: How To Transfer Squarespace Domain To Godaddy
Are Dns Queries Private
Another important DNS security issue is user privacy. DNS queries are not encrypted. Even if users use a DNS resolver like that does not track their activities, DNS queries travel over the Internet in plaintext. This means anyone who intercepts the query can see which websites the user is visiting.
This lack of privacy has an impact on security and, in some cases, human rights if DNS queries are not private, then it becomes easier for governments to censor the Internet and for attackers to stalk users’ online behavior.
are two standards for encrypting DNS queries in order to prevent external parties from being able to read them. Cloudflare DNS supports both of these standards. Cloudflare also partners with other organizations to help improve DNS security for example, helping Mozilla enable DNS over HTTPS in its Firefox browser in order to protect users.
Sales
Joining Or Leaving A Domain
If your computer is part of a domain, joining or leaving the domain wont generally be your job. If your computer needs to be on a domain, it will already be on a domain when its handed to you. Youll usually need the domain administrators permission to leave a domain, so people who sit down to use a domain-joined PC cant just leave the domain. However, you can leave a domain if you have local administrator access on your PC. You wont have administrator access if youre using a locked-down PC, of course.
If you have an old computer thats joined to a domain and you no longer have access to the domain, you can always gain access to the PC by reinstalling Windows. The domain settings are tied to your installed operating system, and reinstalling Windows will give you a fresh system. You shouldnt do this to a work or school PC you dont own, of course!
Domains limit what you can do on your PC. When your computer is part of a domain, the domain controller is in charge of what you can do. This is why theyre used on large corporate and educational networks they provide a way for the institution that provides the computers to lock them down and centrally administer them.
Thats the core concept, although much more can be done with domains. For example, group policy can be used to remotely install software on computers joined to a domain.
Read Also: Who Owns Domain Name Checker
Security Implications For Dns
DNS is a core component of modern networking, and as such, is a rather attractive target for many attackers. When the DNS architecture was developed, security was not included as part of the design. There was nothing designed into the architecture for peer authentication, origin authentication, or data encryption. Some recent advancements in DNS have helped to alleviate some of the current security concerns, but they have not been able to remove them altogether.
The dangers of DNS are well publicized and well documented, owing to its long life on the Internet. More information on these security threats, how they are performed, and how to protect your DNS servers can be found at www.dnssec.net/dns-threats.php. There is also an RFC on DNS Threats, published as RFC 3833. Several types of attacks should be kept in mind regarding your DNS deployment, and some best practices can be employed to help lessen your exposure:
Anatomy Of A Domain Name
Domain names are typically broken up into two or three parts, each separated by a dot. When read right-to-left, the identifiers in domain names go from most general to most specific. The section to the right of the last dot in a domain name is the top-level domain . These include the generic TLDs such as .com, .net, and .org, as well as country-specific TLDs like .uk and .jp.
To the left of the TLD is the second-level domain and if there is anything to the left of the 2LD, it is called the third-level domain . Lets look at a couple of examples:
For Googles US domain name, google.com:
- .com is the TLD
- google is the 2LD
But for Google UKs domain name, google.co.uk:
- .com is the TLD
- .co* is the 2LD
- google is the 3LD
*In this case the 2LD indicates the type of organization that registered the domain
You May Like: Where To Get Gg Domains
Understanding The Domain Name And Ip Address
Now, if you would ask what is domain? Its used to identify various websites and services on the internet. Take the domain name, www.google.com. The naming convention moves from right to left and vice-versa for IP addresses. In the domain name for Google, first, the DNS will check for com which stands for the commercial domain, and is a top-level domain.
Proceeding further, Google is a sub-domain to com, and subsequently, www is a sub-domain to the Google domain. The dot is used to separate the domains from their sub-domains. The full domain name can only consist of 253 characters.
Now, if someone wants to know the domain name registered against an IP address, they will request the DNS server with the IP address of the website. Say the IP address sent is 31.13.79.246, the DNS will first check 31, then 13, then 79, and finally 246, concluding that the IP address belongs to www.fb.com.
The DNS resembles the hierarchy structure of a tree, not the biological one. There is a different tree in computer data structures, in which the address 31 belongs to the top position of the tree and is the primary domain in the hierarchy, addresses 13, 79, 246 are consecutive sub-domains.
The number 246 refers to the server machine hosting the website www.fb.com. All these domain and sub-domain things are not as complicated as you think, but itll take some time to get it correctly if youre new to this concept.
Also Read: What Is HTTP/2 And How It Works
A Brief History Of Dns

When the internet was very, very small, it was easier for people to correspond specific IP addresses with specific computers, but that didnt last for long as more devices and people joined the growing network. It’s still possible to type a specific IP address into a browser to reach a website, but then, as now, people wanted an address made up of easy-to-remember words, of the sort that we would recognize as a domain name today. In the 1970s and early ’80s, those names and addresses were assigned by one person Elizabeth Feinler at Stanford who maintained a master list of every Internet-connected computer in a text file called HOSTS.TXT.
This was obviously an untenable situation as the Internet grew, not least because Feinler only handled requests before 6 p.m. California time, and took time off for Christmas. In 1983, Paul Mockapetris, a researcher at USC, was tasked with coming up with a compromise among multiple suggestions for dealing with the problem. He basically ignored them all and developed his own system, which he dubbed DNS. While it’s obviously changed quite a bit since then, at a fundamental level it still works the same way it did nearly 40 years ago.
You May Like: What Is A .io Website
What Is Domain Name
An internet domain name can be referred as the address of Domain Name Server or a hosting computer server of a web page. Domain names help the visitors to easily memorize company or brand. They are unique in fact.
Different sectors like e-commerce and services use domain names. Most of all, they are even used for blogging, personal branding.
An Example Of a Domain Name
Domain name is a part of a website URL used to access websites, for example:
- Hostname: www
What Are The Types Of Dns Records
DNS Records come in a wide variety of types, each used for different purposes Heres a look at just a few of the most common:
Also Check: What Is The Io Domain Used For
Why Is Dns Security Important
Standard queries, which are required for almost all web traffic, create opportunities for DNS exploits such as DNS hijacking and . These attacks can redirect a websites inbound traffic to a fake copy of the site, collecting sensitive user information and exposing businesses to major liability. One of the best known ways to protect against DNS threats is to adopt the DNSSEC protocol.
Domain Names And Urls
The universal resource locator, or URL, is an entire set of directions, and it contains extremely detailed information. The domain name is one of the pieces inside of a URL. It is also the most easily recognized part of the entire address. When computer users type a web address directly into the field at the top of their browser window, it initiates a process of locating the page requested. To do so, the instructions contained inside the URL, including the domain name, must correctly point to that location. The IP address is a numerical code that makes this possible.
Recommended Reading: How To Find Email Domain And Server