Find The Domain And Range Of Special Functions
Rational Function: A rational function is defined for only the non-zero values of the denominator.
Square Root Function: A square root function is defined for only the non-negative values of the expression under the radical symbol.
How To: Given The Formula For A Function Determine The Domain And Range
What Is An Example Of Finding The Domain And Range Of A Set Of Points
-
State the domain and range of the following relation. Is the relation a function?
The above list of points, being a relationship between certain x‘s and certain y‘s, is a relation. The domain is all the x-values, and the range is all the y-values. To give the domain and the range, I just list the values without duplication:
domain:
range:
Affiliate
While the given set of points does indeed represent a relation , the set they gave me contains two points with the same x-value: and . Since x = 2 gives me two possible destinations , then this relation cannot be a function.
And, when the relation they’ve given me is a set of points, all I need to do is check the points’ x-values if any x shows up more than once, then the relation is not a function. This relation has repeates, so it is:
not a function
Note that all I had to do to check whether the relation was a function was to look for duplicate x-values. If you find any duplicate x-values, then the different y-values mean that you do not have a function. Remember: For a relation to be a function, each x-value has to go to one, and only one, y-value.
-
State the domain and range of the following relation. Is the relation a function?
All I have to do for the domain and range parts of this exercise is list the x-values for the domain and the y-values for the range. I remember to use curly-brace set notation for each:
domain:
range:
this relation is indeed a function.
Content Continues Below
Also Check: How To Register Ie Domain
Determining The Domain And Range Modeled By A Linear Function
To determine the domain of a given situation, identify all possible x-values, or values of the independent variable. To determine the range of a given situation, identify all possible y-values, or values of the dependent variable.
Example 1A clown at a birthday party can blow up five balloons per minute. The relationship between the number of balloons inflated and the time that has passed can be expressed with the equation y = 5x, where x is the number of minutes passed and y is the number of balloons inflated. Find the domain and range of the relations.
In this example, the independent variable is the number of minutes. The possible x-values include all real numbers greater than or equal to 0, since time can be measured in fractional parts of a minute.
The dependent variable is the number of balloons inflated. The possible y-values include all real numbers greater than or equal to 0.
Therefore, the domain is , and the range is .
An Exponential Function: $f = 2^x$
This exponential function can take any value of x we wish to put into it, but it can only return positive values.
Remember that negative exponents don’t mean negative function values. The minus in the exponent just means “take the reciprocal. The reciprocal of a large number is a small number, thus the appearance of the graph.
The domain and range of this exponential function are
$$D: \: \phantom R: \: $$
Don’t Miss: How To Transfer Google Domain To Another Google Account
Domain And Range Of An Absolute Value Function
The function y=|ax+b| is defined for all real numbers. So, the domain of the absolute value function is the set of all real numbers. The absolute value of a number always results in a non-negative value. Thus, the range of an absolute value function of the form y= |ax+b| is y R | y 0. The domain and range of an absolute value function are given as follows
Example: |6-x|
- Domain: The domain of the function is the set R.
- Range: We already know that the absolute value function results in a non-negative value always. i.e., |6-x| 0, for all x.
Polynomial Functions Of Even Degree
Polynomial functions of even degree always have a global maximum or minimum, depending on the sign of the leading term.
Therefore the ranges of polynomials of even degree are determined by the location of that local min. or max.
We won’t always know the exact location of that max. or min. That’s a problem that calculus will help you with later. In such cases, it’s OK just to give that max. or min. a label like we did in the graph, . The minimum value of the function is just b , and we write the domain and range like this:
$$D: \ \ \ R: \ $$
Domain & range of polynomial functions
The range of any polynomial function of odd degree is y = .
The range of a polynomial function of even degree is bounded either from below or above because the function will always have a maximum or minimum value.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is A Domain Website
How To Find Domain And Range Of A Function Without Graphing
How to find domain and range of a function without graphing ?
Here we are going to see how to find domain and range of a function without graphing.
What is domain ?
The domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable.
In other words, the domain of f is the set of all those real numbers for which f is meaningful.
For example, let us consider the function
f = /
The above function accepts all real values except -1 and 1.If we apply x = 1 and -1, the function will become meaningless.
Hence the domain of the given function is R –
What is range ?
The range of real function of a real variable is the step of all real values taken by f at points in its domain.
To find the range of the real function, we need to follow the steps given below.
Step 1 :
Solve the equation y = f for x in terms of y. Let x = g
Step 3 :
Find the values of y for which the values of x, obtained from x = g are real and its domain of f.
Step 4 :
The set of values of y obtained in step 3 is the range of the given function.
Let us look into some example problems to understand the above concept.
Example 1 :
Find the domain and range of the following function
f = x /
Domain of the function f :
f = x /
The denominator will never become zero for any values of x.
Thus f accepts all real values of x.
Hence the domain of the given function is R.
Domain of the function f :
y = x /
Solving for x, we get
x = 1 ± / 2y
Clearly, x will assume real values if
1 – 4y2 0 and y 0
y –
How To Find The Domain And Range Of A Relation
A relation is an asset of x and y coordinates. To find the domain and range in a relation, just list the x and y values, respectively.
Lets see a few examples below to understand this scenario.
Example 10
State the domain and range of the relation
Solution
List the x values. Domain:
List the y values. range:
Example 11
Find the domain and range of the relation
Solution
The domain is and the range is
Example 12
Given that R = , find the domain and range of R.
Solution
The domain is a list of first values, therefore, D= and the range =
Also Check: How To Move A Domain Name
What Is An Example Of Finding The Domain And Range Of A Rational Function
-
Determine the domain and range of the following rational function:
The domain is all the values that x is allowed to take on. The only problem I have with this function is that I need to be careful not to divide by zero. So the only values that x can not take on are those which would cause division by zero. So I’ll set the denominator equal to zero and solve my domain will be everything else.
x2x 2 = 0
x = 2 or x = 1
Then the domain is “all x not equal to 1 or 2″.
The range is a bit trickier, which is why they may not ask for it. In general, though, they’ll want you to graph the function and find the range from the picture. In this case:
As you can see from my picture, the graph “covers” all y-values that is, the graph will go as low as I like, and will also go as high as I like. For any point on the y-axis, no matter how high up or low down, I can go from that point either to the right or to the left and, eventually, I’ll cross the graph. Since the graph will eventually cover all possible values of y, then:
the range is “all real numbers”.
-
Determine the domain and range of the given function:
The domain is all values that x can take on. The only problem I have with this function is that I cannot have a negative inside the square root. So I’ll set the insides greater-than-or-equal-to zero, and solve. The result will be my domain:
2x + 3 0
-
Determine the domain and range of the given function:
y = x4 + 4
Affiliate
the domain is “all x“.
The range is “all y 4″.
How To Find The Range Of A Function
The range is the set of images of the elements in the domain.
To find the range of a function:
- Step 1: Write down the function in the form \\)
- Step 2: Solve it for \ to write it in the form, \\)
- Step 3: The domain of the function \\) is the range of \\).
Example: For the function \=\log x\), the image takes up the values from \ to \. That is, the range of the function is the set of all real numbers.
Don’t Miss: Where Should I Register My Domain Name
How To Find The Domain And Range Of Function Algebraically
Let the function be y=f. Let us find the domain and range of this function algebraically.
To calculate the domain of the function, we simply solve the equation to determine the values of the independent variable x. To calculate the range of the function, we simply express x as x = g and then find the domain of g.
Finding The Domain Of A Function Defined By An Equation
In Functions and Function Notation, we were introduced to the concepts of domain and range. In this section, we will practice determining domains and ranges for specific functions. Keep in mind that, in determining domains and ranges, we need to consider what is physically possible or meaningful in real-world examples, such as tickets sales and year in the horror movie example above. We also need to consider what is mathematically permitted. For example, we cannot include any input value that leads us to take an even root of a negative number if the domain and range consist of real numbers. Or in a function expressed as a formula, we cannot include any input value in the domain that would lead us to divide by 0.
We can visualize the domain as a holding area that contains raw materials for a function machine and the range as another holding area for the machines products ).
We can write the domain and range in interval notation, which uses values within brackets to describe a set of numbers. In interval notation, we use a square bracket \). We will discuss interval notation in greater detail later.
Before we begin, let us review the conventions of interval notation:
- The smallest term from the interval is written first.
- The largest term in the interval is written second, following a comma.
- Parentheses, \ or \\), are used to signify that an endpoint is not included, called exclusive.
- Brackets, \, are used to indicate that an endpoint is included, called inclusive.
Don’t Miss: How To Create Your Own Website Domain For Free
Domain And Range Of Exponential Functions
The function y = ax, a 0 is defined for all real numbers. Hence, the domain of the exponential function is the entire real line. The exponential function always results in a positive value. Thus, the range of the exponential function is of the form y= |ax+b| is y R , . Domain = R, Range =
Example: Look at the graph of this function f: 2x
Observe that the value of the function is closer to 0 as x tends to but it will never attain the value 0. The domain and range of an exponential functions are given as follows:
- Domain: The domain of the function is the set R.
- Range: The exponential function always results in positive real values.
Find The Domain And Range From Graphs
We know that the domain of a function is the set of all input values. So, the domain on a graph is all the input values shown on the \-axis. To find the domain, we need to analyse what the graph looks like horizontally. Moving from left to right along the \-axis, identify the span of values for which the function is defined.
Similarly, the range of a function is the set of all output values. On a graph, this is identified as the values that are taken by the dependent variable \. So, to find the range, look at the set of values that the graph spreads vertically. Those looking for the domain and range calculator should take help from the figures shown on this page.
Consider the graph of the function \.
Looking at the horizontal and vertical spread of the graph, the domain, and the range can be calculated as shown below.
The closed points on either end of the graph indicate that they are also part of the graph. Therefore, the domain is \ and the range is \.
Now, if you have open points instead, the function is not defined at that point.
Here, the domain is \ and the range is \. Note that, here the value \ is included in the range as it already has a pre-image at \ and \
Sometimes the graph continues beyond the portion shown. In such cases, the domain and range could be greater than the visible values.
Also Check: How Do I Transfer My Domain From Squarespace To WordPress
Find The Domain Of A Rational Function
A Rational Function is a fraction of functions denoted by
f=\frac, h\neq 0
Rational function is also called Quotient Function.
Example:
Let f=\frac+3x+2}. Find the domain of f.
Solution:
See that x+2 is defined for all x\epsilon \mathbb.
So we do not have to worry for this part.
From Rule 2 we know that the function f=\frac is defined when h\neq0.
In this problem, we have to find at what points x^+3x+2\neq 0.
Now x^+3x+2\neq 0
i.e., \neq 0
i.e., either \neq 0 or \neq 0
i.e., either x\neq -2 or x\neq -1
Therefore f=\frac+3x+2} exists for all x\epsilon\mathbb except x\neq -2 and x\neq -1
\therefore domain of f = :x\neq -2,-1}.
On the Real axis, the green lines are the domain of f.
We can write this as,
Domain of f=\cup\cup.
Example:
How do you find the domain of the rational function given below
f=\frac+2}
Solution:
For f to be defined,
or, x^\neq -2
or, x\neq \pm \sqrt
or, x\neq \pm \sqrti \epsilon \mathbb, an imaginary number .
This implies that f exists for all x\epsilon \mathbb
\therefore the domain of the function f=\frac+2} is
D=\mathbb=.
Finding Domain Of A Function With A Square Root
Example:
f=\sqrt
Solution:
From Rule 3 we know that a function of the form f=\sqrt is defined when g\geq 0
i.e.,
f=\sqrt is defined when
x+2\geq 0
Putting this result on real line we get
\therefore domain of f=\sqrt is
D=: x\geq -2}=[-2,\infty ).
Example:
Find the domain of the function
f=\sqrt+3x+2}
Solution:
For f to be defined,
i.e., \geq 0
i.e., either x+2\leq 0 or x+1\geq 0
i.e., either x\leq -2 or x\geq -1
Why we write x\leq -2 and x\geq -1?
See the table given below to understand this
| Value of x | Sign of | \geq 0 satisfied or not | |
|---|---|---|---|
| x=-3 | |||
| i.e., x\epsilon | +ve | i.e., +ve |
From the table we can see that the relation \geq 0 is satisfied when
x\epsilon , x=-2, and x=-1, x\epsilon
i.e., x\epsilon
i.e., x\epsilon
\therefore domain of f=\sqrt+3x+2} is
D = \: x \: \epsilon \:
\: \: \: \: \: \: \: \: \: \: = :x\leq -2,x\geq -1}
Also Check: How Do I Get A Domain For My Website
How To Find The Range Of A Quadratic Function
Now for the range. Well use a similar approach, but now we are only concerned with what the graph looks like vertically.
As you can see, outputs only exist for \-values that are greater than or equal to 0. In other words, there are no outputs below the \-axis. We would say the range is all real numbers greater than or equal to 0.
Lets generalize our findings with a few more graphs.
The range for this graph is all real numbers greater than or equal to 2.
The range here is all real numbers less than or equal to 5.
The range for this one is all real numbers less than or equal to -2.
And the range for this graph is all real numbers greater than or equal to -3.
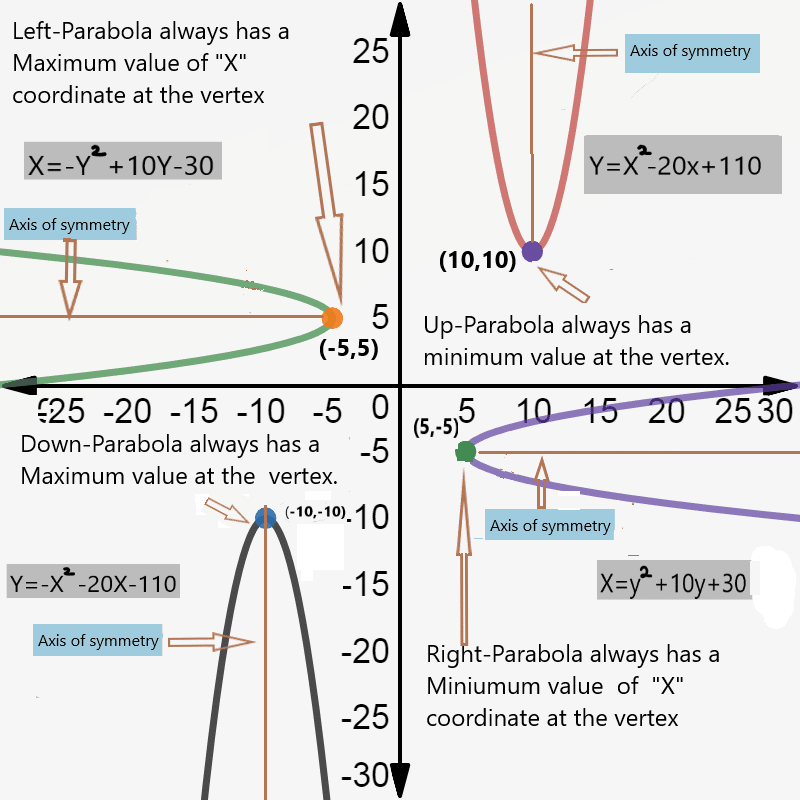
As you can see, the turning point, or vertex, is part of what determines the range. The other is the direction the parabola opens. If a quadratic function opens up, then the range is all real numbers greater than or equal to the \-coordinate of the range. If a quadratic function opens down, then the range is all real numbers less than or equal to the \-coordinate of the range.
Graphs can be helpful, but we often need algebra to determine the range of quadratic functions. Sometimes, we are only given an equation and other times the graph is not precise enough to be able to accurately read the range.